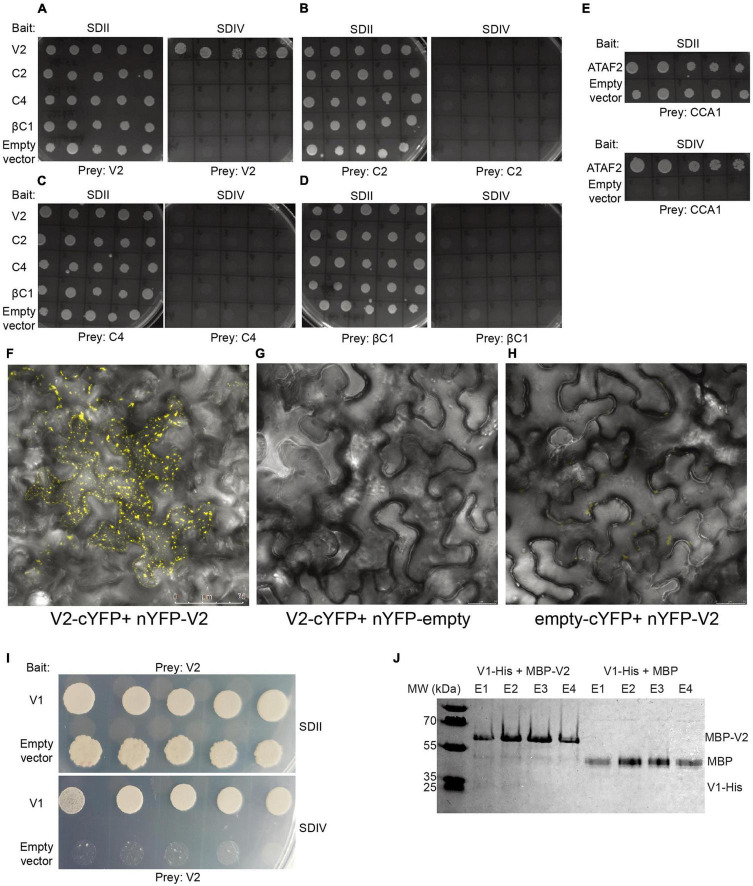
FIGURE 7.
CYVMV V2 physically interacts with itself and V1. When testing the self and mutual interactions among all four silencing suppressors V2 (A), C2 (B), C4 (C), and βC1 (D) via targeted Y2H, only V2 exhibits self-interaction. Empty bait vector pBTM116-D9 was used as the negative control. A known interaction between Arabidopsis CCA1 and ATAF2 was used as a positive control (E). All combinations can grow on SDII plates deprived of leucine and tryptophan, as the bait and prey vectors provide the biosynthesis ability of these two amino acids. Only the positive V2-V2 combination can grow on synthetic dropout IV (SDIV) plates, which indicates their physical interaction. The interaction increases the ability of uracil and histidine biosynthesis in yeast cells and thereby enables their growth on SDIV deprived of uracil, histidine, leucine, and tryptophan. Five independent yeast clones were shown for each combination. Self-interaction of V2 was further confirmed by the in planta bimolecular fluorescence complementation (BiFC) approach. (F) N. benthamiana leaves infiltrated with V2-cYFP + nYFP-V2 constructs showed strong yellow fluorescent signals. As negative controls, no fluorescence was detected in leaves infiltrated with V2-cYFP + nYFP-empty (G) or empty-cYFP + nYFP-V2 (H). (I) CYVMV V1 and V2 proteins physically interact with each other in a targeted Y2H assay. Five independent yeast clones were shown. (J) V1-V2 interaction was confirmed in a pull-down assay. V1-His + MBP-V2 and V1-His + MBP protein mixtures were loaded to pass through the amylose resin, respectively. After washing away unbound proteins, four rounds of elution (E1-E4) were performed to collect maltose-binding proteins and their interactors. V1-His and MBP-V2 were co-eluted from the amylose resin (E1 and E2). In contrast, the MBP tag protein cannot bind V1-His. YFP, yellow fluorescent protein.