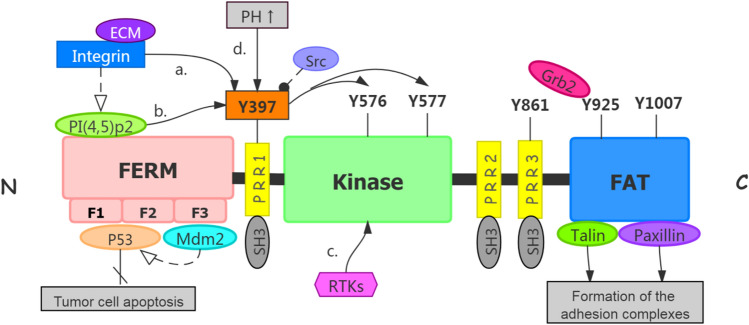
Fig. 1.
structure of FAK protein and activation of FAK. 1.1 The protein structure of FAK which contains three major domains and three PPR small domains between the three major domains. 1.2 The activation of FAK. a Integrin binding to the relevant ligand on the extracellular matrix leads to Tyr397 autophosphorylation of FAK and FAK activation [16]. b Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate [PI(4,5)P2] binds to FERM mediated by integrins, the Tyr397 phosphorylation site is exposed and autophosphorylated [17]. Tyr397 phosphorylation recruits Src, which further phosphorylates Tyr576 and Tyr577 to release kinase domain from PERM domain, to make FAK reaches a fully activated state. c The receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs) can directly activate the phosphorylation activation loop in FAK kinase region, thereby upregulating FAK kinase activity [18]. d Elevation pH reduces the stability of the FERM/kinase region interaction, resulting in phosphorylation of Y397 [19]. Activated FAK arrested p53 or convene Mdm-2 to enhance ubiquitination of p53 to block apoptosis in tumor cells. Talin and Paxillin bind to integrins in cytoplasmic regions, which can mediate the formation of adhesion complexes [1].