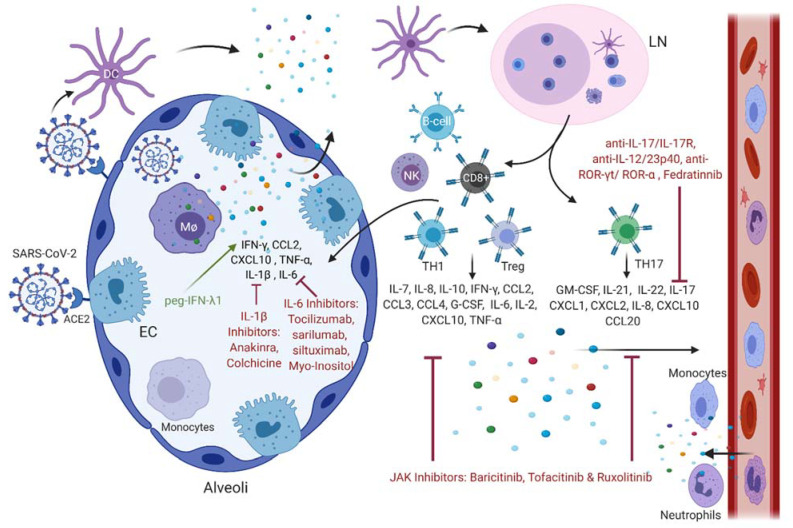
Figure 1.
Innate and adaptive immune cells involved in SARS-CoV-2 infection, as well as the different chemokines and cytokines released and their inhibitors. SARS-CoV-2 binds ACE2 receptor on epithelial cells (ECs) and on macrophages (MΦ) of the alveoli. This triggers the release of cytokines and chemokines that attract more immune cells to the injured lung. Upon infection, activated DCs migrate to the lymph node (LN), where they activate T- and B-lymphocytes, which will further release pro-inflammatory mediators that exacerbate the infection. Several drugs currently used on patients or being tested in clinical trials target the various chemokines and cytokines responsible for the cytokine storm in COVID-19, including IL-6 inhibitors, INF, IL-1β inhibitors, JAK inhibitors, and IL-17 antibodies.