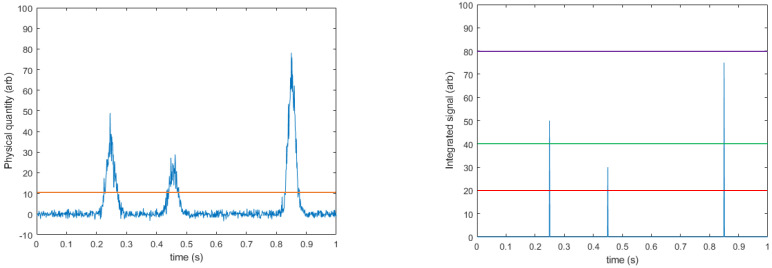
Figure 3.
Basic principles behind PC approaches. (LEFT) Some physical feature of the system, such as the charge in a pixel, is shown varying continuously (blue line). Some level of noise is always present in these measurements; however, when a photon interacts with the detector material it causes a sharp and significant change in the measured quantity. A threshold is set (orange line) sufficiently above the noise floor such that any signal rises above this level indicate a photon interaction. A counter is then linked to this threshold and incremented whenever the threshold is crossed from below. The physical quantity then returns to baseline over some time, dt. (RIGHT) By using multiple threshold-counter pairs, the energy of each event can be broadly binned. In this example the counter associated with the lowest threshold (red line) would be incremented three times, the middle threshold counter (green line) incremented twice, and the highest-energy threshold counter (purple line) not incremented at all. The number of events between given thresholds is then determined by subtraction of adjacent counters. Adapted with permission from ref. [32]. Copyright 2021 The Institute of Cancer Research.