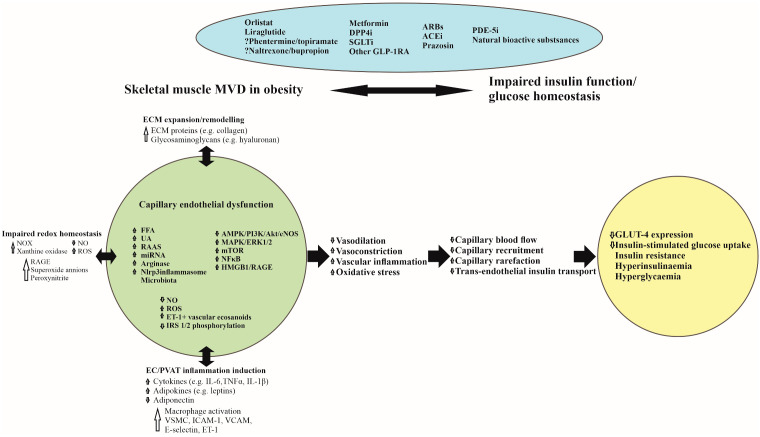
Figure 1.
Pathophysiological mechanisms linking skeletal muscle microvascular dysfunction with glucometabolic disorder in obesity and potential therapeutic agents. ACEi, Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme inhibitors; AMPK 5’-, Adenosine Monophosphate-activated Protein Kinase; ARBs, Angiotensin Receptor Blockers; Akt, Protein Kinase B; DPP4i, Dipeptidyl-Peptidase-4 inhibitors; EC, Endothelial Cell; ECM, Extracellular Matrix; eNOS, endothelial Nitric Oxide Synthase; ERK, Extracellular-signal-regulated Kinase; ET-1, Endothelin 1; FFA, Free Fatty Acids; GLP-1RA, Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists; GLUT-4, Glucose Transporter 4; HMGB 1, High Mobility Group Box chromosomal protein 1; IRS, Insulin Receptor Substrate; ICAM1, Intercellular Adhesion Molecule 1; IL-1β, Interleukin-1Beta; IL-6, Interleukin-6; MAPK, Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase; miRNAs, Micro RNAs; mTOR, Mammalian Target of Rapamycin; MVD, Microvascular Dysfunction; NF-κB, Nuclear Factor-Kappa B; NO, Nitric Oxide; NOX, Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide Phosphate (NADPH) Oxidase; PDE-5i, Phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitors; PI3K, Phosphatidylinositol 3 Kinase; RAAS, Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System; ROS, Reactive Oxygen Species; RAGE, Receptor for Advanced Glycation End products; SGLT2i, Sodium Glucose co-Transporter 2 inhibitors; TNF-α, Tumour Necrosis Factor-alpha; UA, Uric Acid; VCAM1, Vascular Cell Adhesion Molecule 1; VSMC, Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells.