Figure 5.
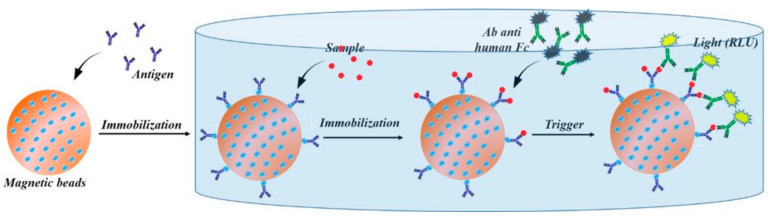
CLIA-based diagnostic assay principle. Purified VZV-gE antigen is immobilized onto metal beads and saturated with BSA. In the machine, a small amount of controls or test samples are added to the test tube and incubated. The test tube is washed to remove any unbound human immunoglobulin (h-Ig). A pre-labeled anti-human Ig conjugate is added to the test tubes. Then, a prepared substrate is added and catalyzed by the pre-labeled enzyme to produce a fluorescence, which is directly proportional to the amount of human anti-antigen Ig captured on the beads.