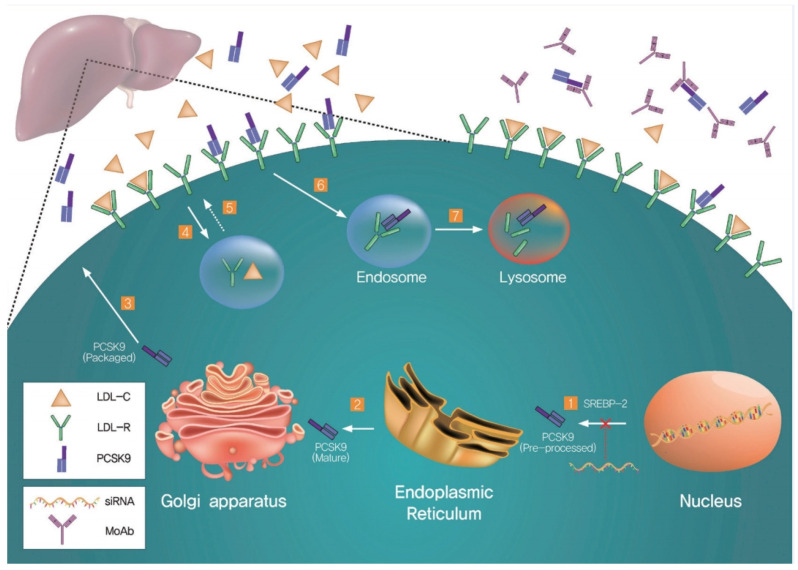
Figure 2.
PCSK9-mediated regulation of LDLRs and representative therapy targets (Cho KH, Hong YJ, 2020, [55]). (1) SREBP-2 enhances transcription of both LDLRs and PCSK9. PCSK9 is processed in the ER (2) and stored in the Golgi apparatus (3) before secretion. LDLRs bind the LDL cholesterol (LDL-C) on the cell surface and this complex is internalized via endocytosis (4). LDL-C leaves LDLRs and LDLRs are recycled on the cell surface (5). Secreted PCSK9 binds to LDLRs and the complex is captured in the endosome (6) leading to LDLR lysosomal degradation (7). There are two major approaches to inhibit PCSK9: using siRNA and PCSK9-specific monoclonal antibodies (MoAbs). The siRNA inhibits PCSK9 translation (lower right), whereas MoAbs block the binding of PCSK9 to surface-expressed LDLRs (upper right). An especially attractive alternative would be the discovery of orally bioavailable low-molecular PCSK9 inhibitors which are economically more feasible than the mAbs.