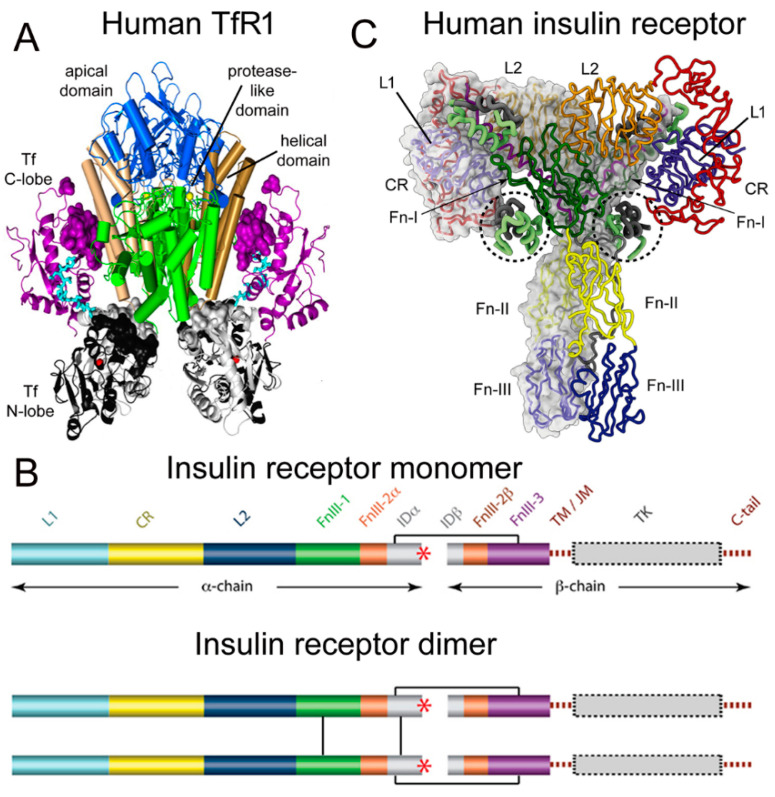
Figure 1.
(A) Three-dimensional structure of the complex of the human TfR ECD and holo-Tf. The tetrameric complex is comprised of 2 TfRs and 2 holo-Tf molecules. The cell surface is at the bottom of the structure and the apical domain (blue) is at the top; the 2 protease-like domains are shown in green and the helical domain is shown in brown/tan. The N-lobe and C-lobe of Tf are shown in gray/black and purple, respectively. The Fe+3 bound within the N-lobe is shown in red; the linker between the N and C lobes of Tf is cyan. Reproduced with permission from [37]. (B) Two-dimensional structure of the human IR as a monomer (top) and a dimer (bottom). A single disulfide bond joins the alpha and beta chains of each monomer, and the dimer is formed by 2 disulfide bonds between each alpha chain. Reproduced from [42], Copyright© 2011 licensed under Creative Commons Attribution License (CC-BY). (C) Three-dimensional structure of the complex of the human IR and insulin. The structure is comprised of the IR dimer and 4 bound insulin molecules. Insulin bound to the second site formed by the FnIII-1/FnIII-2 domains is encircled. Reproduced with permission from [43], Copyright© 2021 Elsevier, as reported in [44]. The IR domains in panels B and C are defined in the text.