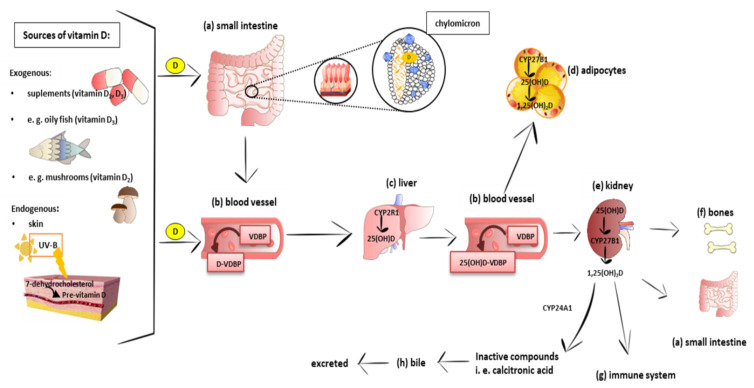
Figure 1.
Schematic absorption, distribution, metabolism, and clearance of vitamin D indicating the strategic tissues/organs involved (a–h) and sources of the molecule. Main exogenous source of vitamin D are oily fish and mushrooms, apart from pharmaceutical supplements. The other source of the molecule is its synthesis in the epidermis layer of the skin. Under the influence of ultraviolet (UVB) radiation, 7-dehydrocholesterol undergoes nonenzymatic photoisomerization into pre-vitamin D. Next, pre-vitamin D is transformed into cholecalciferol in a heat-dependent process and comes out of the skin to the blood and binds to vitamin D-binding protein (VDBP) (b). Vitamin D from the diet is transported in blood mainly in chylomicrons (a). Next, both skin and diet-derived vitamin D reach the liver (c) and is hydroxylated into 25(OH)D (calcidiol) by 25-hydroxylase (CYP2R1). 25(OH)D leaves the liver and is bound to VDBP (b), which presents the highest affinity to calcidiol. 25(OH)D-VDBP is the major circulating form of vitamin D. Then, calcidiol is internalized by target tissues, mostly the kidneys (e), where it is transformed into the active form 1,25(OH)2D (calcitriol) by 1-hydroxylase (CYP27B1). CYP27B1 is expressed not only in the kidneys but also in numerous different cells, including adipocytes (d). The main function of vitamin D is to regulate calcium and phosphate homeostasis. The two main effector organs related to this function, on which the active metabolites of vitamin D act, are the intestines (a) and bones (f), and the molecule also exerts immunomodulatory effects (g). Calcitriol is able to stimulate its own degradation by the induction of 25(OH)D-24-hydroxylase (CYP24A1). CYP24A1 is an enzyme degrading both calcitriol and its precursor calcidiol to biological inactive metabolites, including calcitroic acid, which is excreted with bile (h). Abbreviations: D2, egrocalciferol, plant origin vitamin D; D3, cholecalciferol, animal origin food vitamin D; UVB, ultraviolet radiation; SR-B1, scavenger receptor class B type 1; CD36, class B scavenger receptor; NPC1-L1, Niemann-Pick C1-Like 1; CYP2R1, cytochrome P450 family 2 subfamily R member 1; CYP24A1, cytochrome P450 family 24 subfamily A member 1; CYP27B1, cytochrome P450 family 27 subfamily B member 1; CYP24A1, cytochrome P450 family 24 subfamily A member 1.