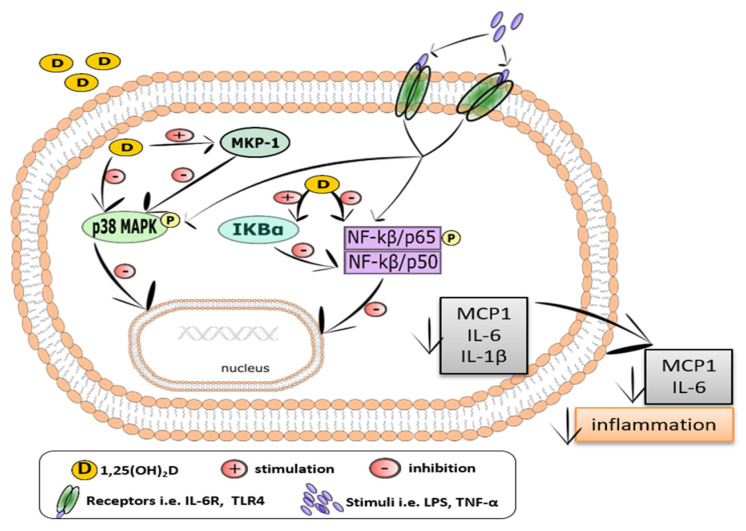
Figure 4.
The effect of vitamin D on the MAPK and NF-kB pathways engaged in adipocyte inflammation. NF-κB is a key transcriptional factor involved in multiple processes, e.g., proliferation but also at the first step in the regulation of the inflammatory response due to controlling the release of antimicrobial molecules, including cytokines and chemokines, also in pre-adipocytes and adipocytes, where vitamin D was found as an inhibitor of the processes NF-κB- and MAPK-driven. Abbreviations: MKP-1, MAPK phosphatase-1; p38 MAPK, p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase; IKBα, nuclear factor-κappa B inhibitor alpha; MCP1, monocyte chemoattractant protein 1; IL-6, interleukin 6; IL-1β, interleukin 1β; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor α; IL-6R, interleukin 6 receptor; TLR4, Toll-like receptor 4. ↑increase; ↓decrease.