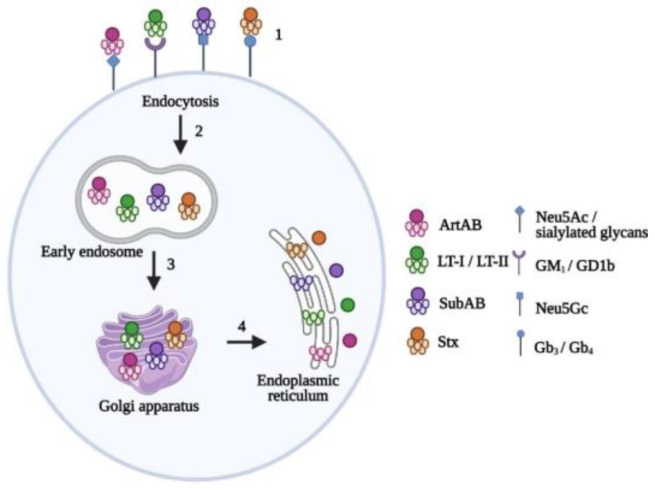
Figure 2.
Retrograde trafficking of AB5 toxins. (1) Holotoxins bind to target receptors on host cells via the B subunit; (2) binding of the B subunit triggers endocytosis of the toxin, forming early endosomes (3) for transport to the Golgi apparatus; (4) toxins migrate to the endoplasmic reticulum, where the B pentamer subunit is cleaved from the A subunit to allow for downstream cytotoxic effects in the cytosol. LT-I/LT-II: heat-labile enterotoxins; SubAB: subtilase toxin; Stx: Shiga toxin; Neu5Ac: N-acetylneuraminic acid; GM1/GD1b: gangliosides; Neu5Gc: α-2-3-linked N-glycolylneuraminic acid; Gb3:globotriaosylceramide; Gb4: globoside. Created in BioRender.com.