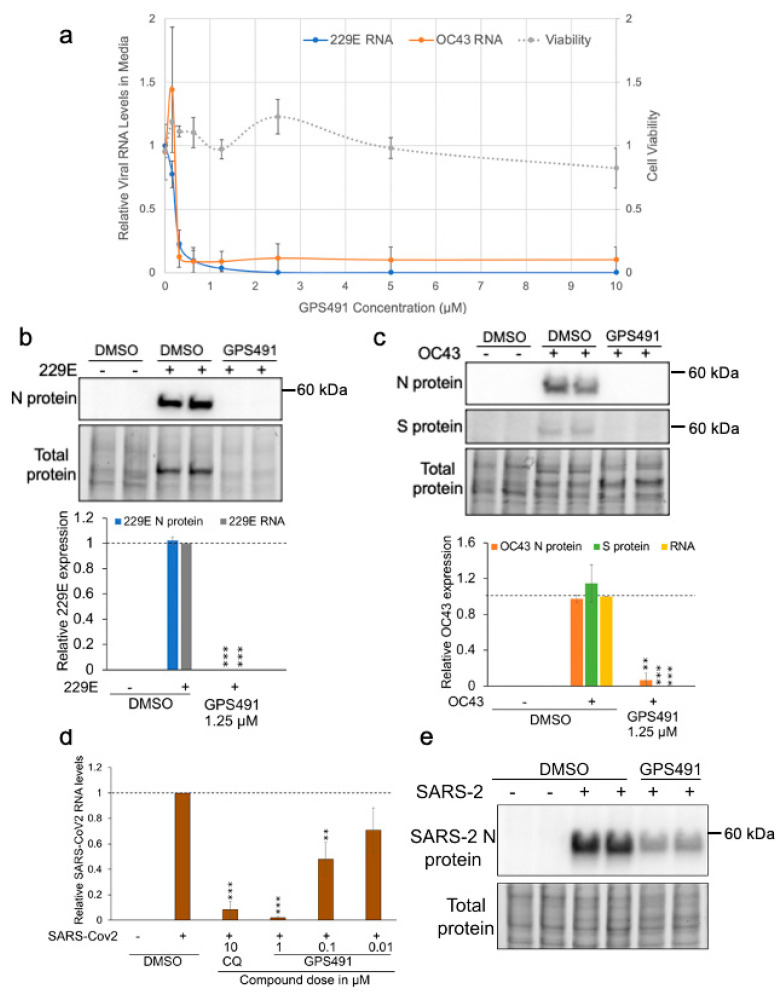
Figure 8.
GPS491 inhibits replication of 229E, OC43, and SARS-CoV2 coronaviruses. (a) Huh7 cells were infected with either 229E or OC43 at an input MOI of 0.1 and 1, respectively, for 1 h. Virus inoculum was removed, cells were washed, and fresh media containing 1% DMSO or varying concentrations of GPS491 (from 0 µM to 10 µM) were added. Then, 2 days p.i (229E) or 4 days p.i. (OC43), media were harvested to quantitate viral genomic RNA levels by RT-qPCR assay. All the values are expressed relative to the values detected in virus-infected DMSO-treated samples. Effect of GPS491 on cell viability was assessed 2 days post compound addition using alamarBlue at the indicated doses of GPS491. Data are indicated as mean ± SD, ** p ≤ 0.01, and *** p ≤ 0.001. (b,c) Huh7 cells were infected with (b) 229E at an MOI of 0.03 or (c) OC43 at an MOI of 0.3 for 1 h after which the virus inoculum was removed, cells were washed with 1× PBS, and media containing 1% DMSO or 1.25 µM GPS491 were added. Cells and media were harvested 2 days (229E) or 4 days (OC43) p.i., and the levels of viral proteins (N, S) were determined by Western blot and virus production was assessed by RT-qPCR of the media (RNA). Shown are representative Western blots and their respective quantitation indicating the effects of GPS491 following infection with 229E and OC43, respectively. Band intensity was quantified relative to virus-infected control and normalized to total protein load (stain-free gels). Data are indicated as mean ± SD and generated from n = 3 independent assays, each performed in duplicate. (d,e) Huh7 cells were infected with SARS-CoV2 at an MOI of 1 for 1 h. Virus inoculum was removed, and fresh media containing DMSO, chloroquine (CQ, 10 µM), or indicated doses of GPS491 were added. Two days post infection, (d) media were harvested, and levels of virion production determined by RT-qPCR or (e) lysates from cells treated with 1% DMSO or 0.3 µM GPS491 were blotted to measure expression of viral N protein. Results shown were generated from n = 3 independent assays.