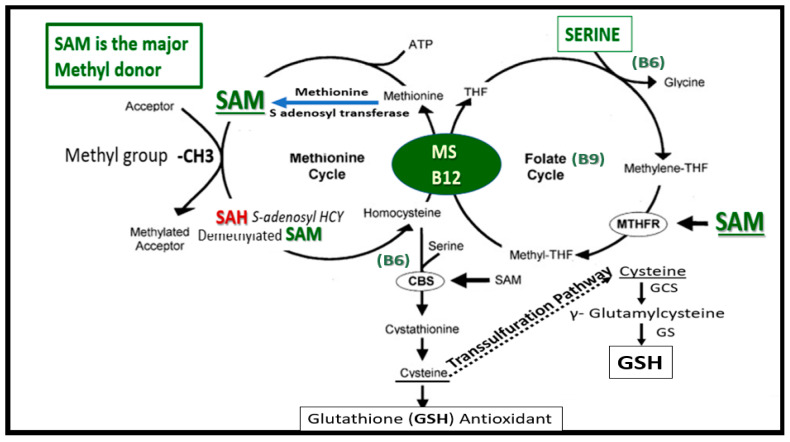
Figure 1.
Folate-Mediated One-Carbon Metabolism (FOCM). This figure illustrates both the folate and methionine interdependent cycles and supports the importance of the methyl donor S-adenosylmethionine (SAM) as well as demonstrating the importance of the essential B vitamins. Importantly, note that methionine and tetrahydrofolate (THF) are derived primarily through dietary intake to supply the methionine and folate cycles and that the enzyme methionine synthase (MS) and its essential cofactor vitamin B12 are placed in a central position of the interconnected folate and methionine cycles. FOCM comprises a network of interconnected folate-dependent metabolic pathways responsible for serine and glycine interconversion, de novo purine synthesis, de novo thymidylate synthesis and homocysteine remethylation to methionine as well as providing antioxidant defense via glutathione (GSH) production via the transsulfuration pathway. Note that the encircled methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR) enzyme plays and important role in the folate cycle. The most common genetic variant in MTHFR gene to date is the 677C > T polymorphism, which results in elevated levels of Hcy especially if there is deficient folate. Once Hcy is synthesized through multiple steps in the methionine cycle, it may then undergo remethylation to methionine or be eliminated through the transsulfuration pathway. Additionally, thymidylate synthase (TYMS) converts deoxyuridine monophosphate (dUMP) to deoxythymidine monophosphate (dTMP) (not shown) in a 5,10-methylene-THF-dependent reaction. Importantly, cystathionine beta synthase (CBS) and cystathionine gamma lyase (CSE-CGL) do not only contribute to generate GSH (antioxidant) in the transsulfuration pathway but also are important for endothelial cell generation of hydrogen sulfide (H2S), a known gaso-transmitter and vasodilator. Elevation of Hcy from the methionine cycle may result in hyperhomocysteinemia, which is an independent risk factor for cerebro-cardiovascular diseases, accelerated atherosclerosis, thromboembolism, hypoxemia and stroke. CBS = cystathionine-beta-synthase; GCS = glutamate cysteine ligase (gamma-glutamylcysteine synthetase); GS = glutathione synthase; GSH = glutathione; MTHFR = methylenetetrahydrofolate; MS = methionine synthase; THF = tetrahydrofolate.