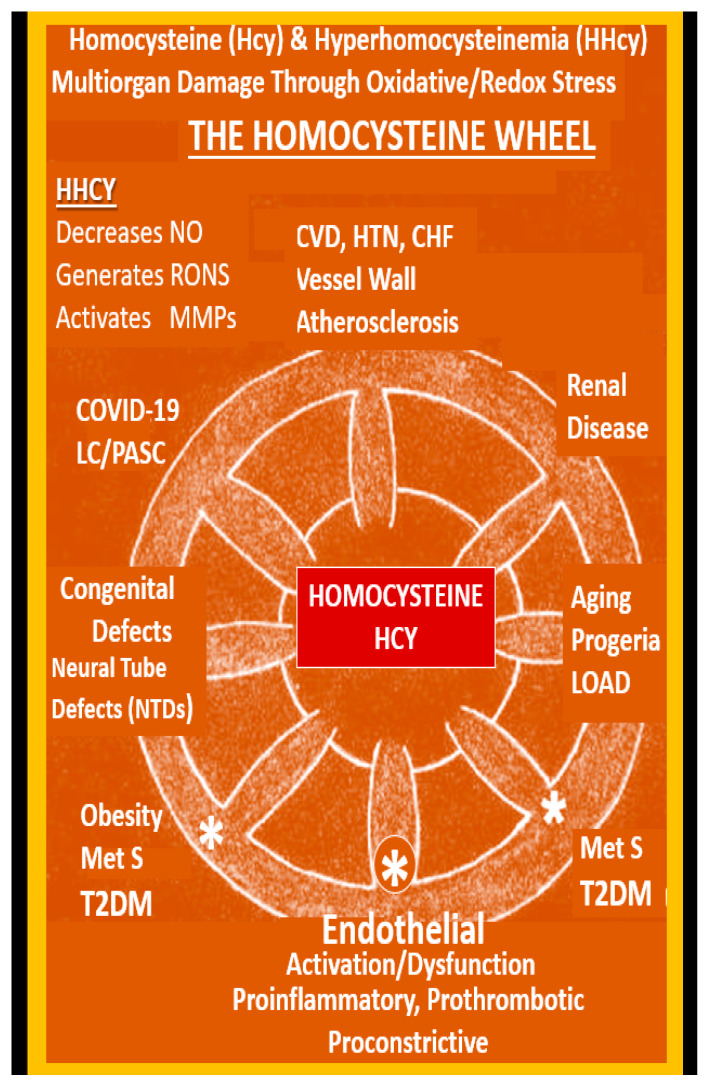
Figure 11.
The Homocysteine Wheel. This illustration depicts the central importance of homocysteine (Hcy) in its hyperhomocysteine (HHcy) state as it relates to the multiorgan tissue damage and associated multiple clinical diseases, which now includes the COVID-19 post-viral syndrome of LC/PASC. HHcy generates damage to proteins, lipids and nucleic acids as result of oxidative redox stress and the generation of excessive reactive oxygen nitrogen species (RONS). In HHcy, Hcy undergoes autoxidation, formation of Hcy mixed disulfides, interaction of Hcy thiolactones and protein homocysteinylation reactions, which result in damage and dysfunction to proteins, tissues and organs. Note the large asterisk at the central bottom of this illustration where the effects of HHcy promotes the uncoupling of the endothelial nitric oxide synthase enzyme (eNOS) by oxidizing the tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4) co-enzyme of eNOS and thus promotes an even further production of superoxide while it concurrently decreases the bioavailability of nitric oxide (NO), thus important to normal endothelial cell dysfunction. As a result, the endothelium undergoes activation and dysfunction and becomes a proinflammatory, prothrombotic endothelium due to increased generation of RONS. While this review has focused primarily on COVID-19 and LC/PASC, this illustration demonstrates that HHcy affects many other tissues, organs and clinical diseases. This modified image is reproduced with permission by CC 4.0 [6]. CHF = congestive heart failure; COVID-19 = coronavirus disease-19; CVD = cebro-cardiovascular disease; HTN = hypertension; MetS = metabolic syndrome; MMPs = matrix metalloproteinases; NTD = neural tube defects; LC/PASC = Long COVID/post-acute sequelae of SARS-CoV-2; LOAD = late-onset Alzheimer’s disease; T2DM = type 2 diabetes mellitus.