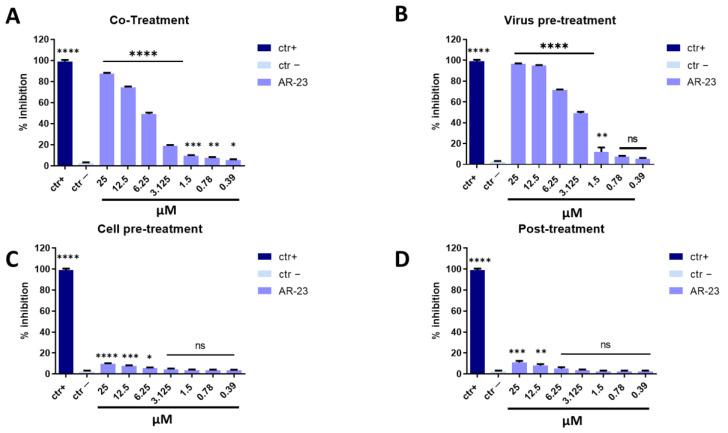
Figure 4.
Antiviral activity against MeV. Different assays were performed in order to evaluate anti-MeV activity. (A) Co-treatment: simultaneous addition of AR-23 and virus to the cells; (B) Virus pre-treatment: virus incubated with the peptide, and then used to infect cells; (C) Cell pre-treatment: AR-23 incubated with the cells before the viral infection; (D) Post-treatment: AR-23 added to the infected cells. Peptide AR-23 inhibited the early stages of infection, acting in co-treatment (A) and virus pre-treatment (B) assays, while it was not able to interact with the cellular surface (C) or block the viral replication (D). Different compounds were used as positive control (ctr+) for each treatment: mucroporin M1 (A,B, 10 μM for both the assays) [40], FIP peptide (C, 20 μM) [41], and 5′-nor carbocyclic adenosine analogue (D, 5 μM) [42], while infected cells were used as negative control (ctr-). **** p < 0.0001; *** p < 0.0002; ** p < 0.0021; * p < 0.021; ns: non-significant.