Table 1.
Important natural products derived from plant and microbial sources in the last few decades with their therapeutic indications and probable mechanism of actions.
| Name of the Natural Compound | Botanical Source | Chemical Structure | Therapeutic Indication/Activities | Mechanism of Action | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drugs Derived from Plant Sources | |||||
| Arglabin | Artemisia glabella |
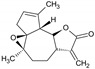
|
Anti-tumor | Inhibition of farnesyl transferase | [21,22] |
| Artemisinin | Artemisia annua L. |
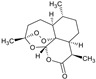
|
Treatment of malaria | Free radical formation that alkylate essential malarial proteins | [23] |
| Cannabidiol | Cannabis sativa L |
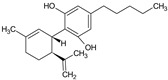
|
Anti-epileptic, anxiolytic, antipsychotic, and anticancer | Modulation of CB1, CB2, 5HT1A receptors in the CNS | [24] |
| Capsaicin | Capsicum annum L.; C. minimum Mill. |
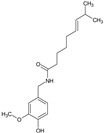
|
Chronic pain syndromes such as postherpetic neuralgia and musculoskeletal pain | Activates Transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 (TRPV1) in sensory nerves | [25] |
| Colchicine | Colchicum spp. |
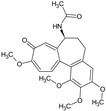
|
Gout | Prevents microtubule assembly and hence modulate multiple pro- and anti-inflammatory pathways | [26] |
| Curcumin | Curcuma longa L. (Turmeric) |
|
Antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, arthritis, metabolic syndrome and pain | Inhibition of NF-kB; scavenge reactive oxygen and nitrogen species; modulates the activities of GSH, catalase and SOD | [27] |
| Epigallocatechin-3-O-gallate (EGCG) | Camellia sinensis L. (Green tea) |
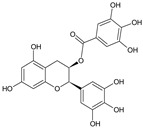
|
Anti-viral against a diverse family of DNA and RNA viruses; antibacterial and antifungal activities. Anticancer, anti-inflammatory and anti-diabetic activities | Alter or damage viral particle, primary target is viral membrane; disruption of lipid layer in bacterial cell wall; inhibits dihydrofolate reductase. Modulation of ROS production and inhibition of NF-kB signaling responsible for anticancer activity | [28,29] |
| Galantamine | Galanthus caucasicus Grossh. |
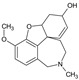
|
Dementia associated with Alzheimer’s disease | Reversible acetylcholinesterase inhibitor; modulation nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (nAChRs) | [30] |
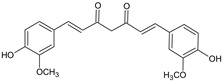
| Genistein | Genista tinctoria L. |
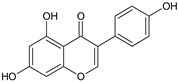
|
Anticancer, Alzheimer’s disease | Protein-tyrosine kinase inhibition, induction of apoptosis, cell cycle arrest, antimetastatic and antiangiogenic activity, antioxidant | [31] |
| Gossypol | Gossypium hirsutum L. (Cotton plant); Thespesia populnea |
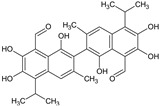
|
Anti-infertility/male contraceptive, Anticancer, antiviral, antimicrobial, antioxidant activities | Inhibit sperm production and motility; Bcl-2 inhibition; DNA polymerase and topoisomerase II inhibition; induce apoptosis | [32] |
| Ingenol mebutate | Euphorbia peplus L. |
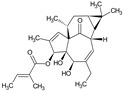
|
Actinic keratosis | Dual mechanism, Inducer of cell death necrosis and local pro-inflammatory response | [33] |
| β-Lapachone | Tabebuia avellanedae (Lapacho tree) |
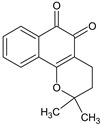
|
Variety of cancers, especially solid tumors, anti-trypanosoma, antimicrobial and antimalarial activities | Anticancer activity through formation of ROS in NQO1-positive cells, topoisomerase inhibition, mTOR pathway modulator | [34,35] |
| Masoprocol | Larrea tridentate |
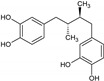
|
Antineoplastic agent used in cancer chemotherapy | 5-Lipoxygenase inhibition | [36] |
| Omacetaxine mepesuccinate (Homoharringtonine) | Cephalotaxus harringtonia; C. fortune |
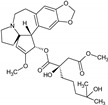
|
Anticancer agent; mainly chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) | Protein synthesis inhibition (prevent peptide elongation) |
[37] |
| Paclitaxel | Taxus brevifolia Nutt. |
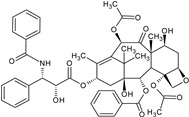
|
Cancer chemotherapy | Mitotic inhibitor | [36,38] |
| Podophyllotoxin | Podophyllum emodi Wall. and P. peltatum L. |
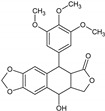
|
Antitumor | Polymerization of tubulin resulting in cell cycle arrest and suppress the formation of mitotic spindles microtubules | [39] |
| Quercetin | Many sources including Allium cepa L.; Morus alba; Camellia sinensis; Moringa oleifera; Centella asiatica etc. |
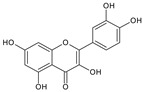
|
Antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anticancer, cardiovascular protection; Alzheimer’s disease; anti-ulcer; antimicrobial; antiallergic | Inhibits cyclooxygenase and lipoxygenase; inhibits platelet aggregation; inhibit gastric secretion and lipid peroxidation; ROS generation and MicroRNA 21 elevation | [40] |
| Resveratrol | Vitis vinifera L |
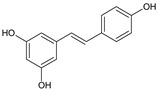
|
Chemopreventive and chemotherapeutic in different types of cancer. Also used as antidiabetic, in cardiovascular complications, metabolic syndromes, antioxidant. | Modulation of multiple molecular pathways involved in cancer and xenobiotic metabolism; reduce oxidative stress and inflammation; cell proliferation arrest; induce apoptosis | [34] |
| Drugs Derived from Microbial Sources | |||||
| Teixobactin | Eleftheria terrace | N-[N-Methyl-D-Phe-Ile-Ser-D-Gln-D-alle-Ile-Ser-]cyclo[D-Thr-Ala-[3-(2-iminoimid-azolidine-4 beta-yl)-Ala-]Ile-] | Antibacterial agent active against various gram-positive bacterial including vacomycin resistant enterococci and methicillin-resistant S. aureus | Inhibition of bacterial cell-wall sybthesis by binging to the synthesis building blocks lipid-II and lipid-III | [41] |
| Lodopyridone | Saccharomonospora sp. |
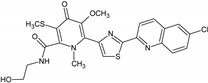
|
Anticancer | Cytotoxic to HCT-116 human colon cancer cells | [42] |
| Salinosporamide A | Salinospora tropica |
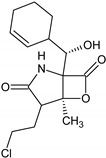
|
Anticancer | Inhibition of 20S Proteasome | [43] |
| Platensimycin | Streptomyces platensis |
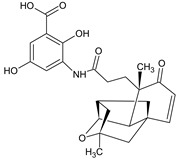
|
Antibiotic, active against various Gram-positive bacteria including resistant strains | Inhibition of fatty acid synthesis in cell membrane through inhibition of β-ketoacy synthases I/II (FabF/B) | [44] |
| Platencin | Streptomyces platensis |
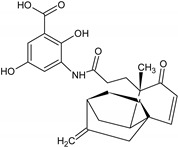
|
Antibiotic, active against various Gram-positive bacteria including resistant strains | Inhibition of fatty acid synthesis in cell membrane through inhibition of β-ketoacy synthases I/II (FabF/B) | [44] |
| Cryptophycin | Cyanobacteria Nostoc sp. |
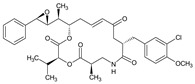
|
Anticancer | Inhibiotion of cell division by depletion of microtubule through interaction with tubulin | [45] |
| Daptomycin | Streptomyces roseosporus | - | Systemic and life-threatening infection caused Gram-positive bacteria | Disruption of bacterial cell-membrane function | [46] |
| Retapamulin | Pleurotus mutilins |
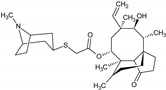
|
Antibacterial used to treat topical skin infection impetigo | Inhibition of bacterial protein synthesis by binding to 50s ribosome | [47] |
