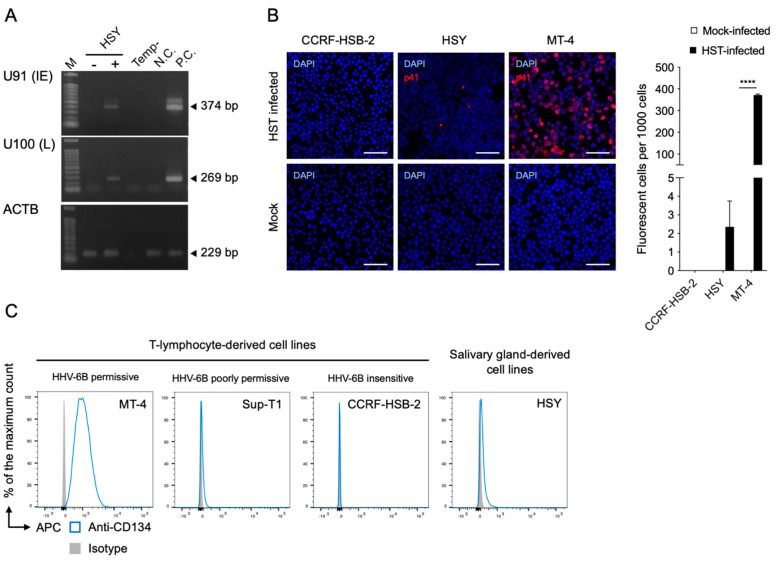
Figure 1.
HHV-6B infectivity in HSY cells and relative CD134 expression. (A) Viral RNA detection in HSY cells using RT-PCR. Cells were infected with HHV-6B HST and total RNA was extracted at 48 h post-infection. U91 (immediate early) and U100 (late) transcripts were detected. β-actin (ACTB) was used as an internal control. M, DNA ladder; -, mock-infected HSY cells; +, HST-infected HSY cells; Temp-, No template control; N.C., negative control (HST-infected CCRF-HSB-2 cells); P.C., positive control (HST-infected MT-4 cells). (B) Viral antigen detection in HSY cells using an immunofluorescence assay. Cells were infected with HHV-6B HST and treated with cold acetone at 48 h post-infection (left panel). HHV-6 p41 protein (red) was detected. Nuclei of cells were stained with DAPI (blue). Scale bars represent 50 μm. Virus-infected cells (red) were counted (right panel). Error bars represent standard deviations (n = 3 per cell). Asterisks indicate statistical significance (**** p < 0.0001, Bonferroni’s multiple comparison test). (C) CD134 expression on T-lymphocyte cell lines and HSY cells was analyzed using fluorescence-activated cell sorting. Cells were stained with APC-conjugated anti-CD134 or isotype control antibodies. The antibody specific signals of the cells are shown in the histogram.