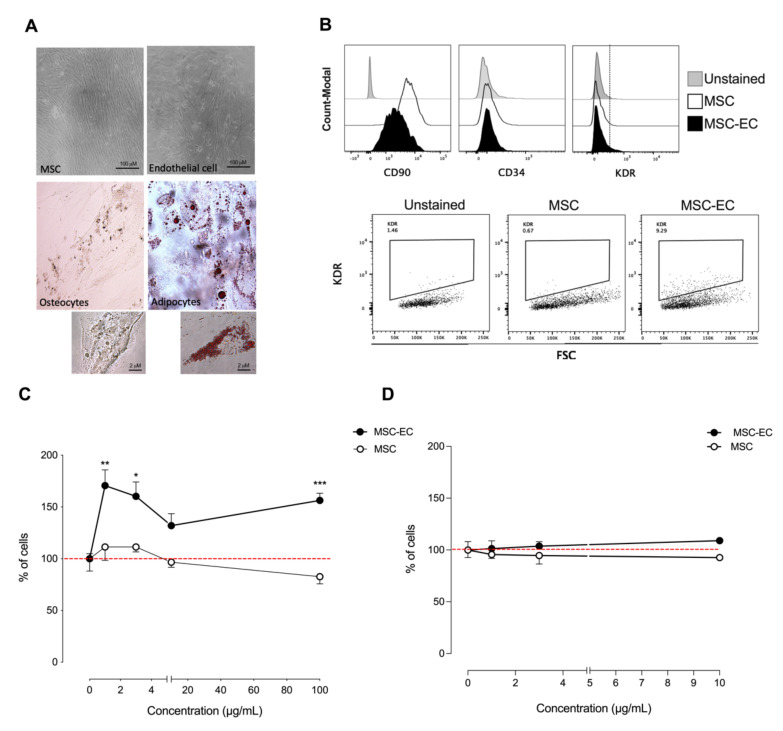
Figure 1.
Phenotypic characterization of human endothelial cell-differentiated mesenchymal stem cells (hMSC-EC) and functional characterization of hMSC-EC-secretome in endothelial-like and keratinocytes cell lines. (A) hMSCs were differentiated into endothelial cells, osteocytes, and adipocytes using different differentiation media. The cells were stained for lipid droplets (Oil Red O staining) or calcium deposits (Von Kossa staining), respectively (B). The expression of CD90, CD34, and KDR was measured in hMSCs and hMSCs-EC after 14 days of culture using flow cytometry. hMSC and hMSC-EC secretome were added into ECV-304 and HaCaT at 1, 3, and 10 μg/mL for 24 h. The % of ECV-304 (C) and HaCaT (D) cells was calculated using the sulforhodamine B (SRB) assay. The values were expressed as a percentage of the control without secretome. The red line corresponds to the basal level. One-way ANOVA followed by a Tukey–Kramer test was used to examine the difference between experimental group. Values are expressed as mean and S.E.M. n = 4. Statistical significance is represented as * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.005 vs. control.