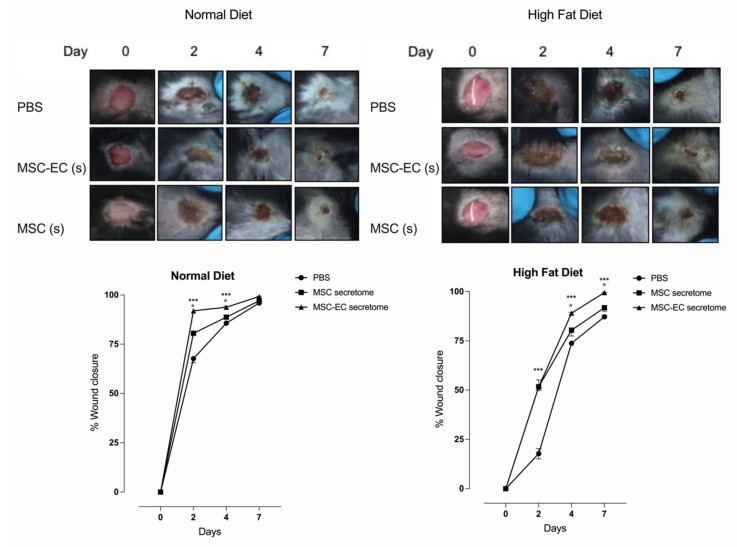
Figure 3.
The effect of human mesenchymal stem cells (hMSCs) and human endothelial cell-differentiated mesenchymal stem cells (hMSC-EC) secretome in wound healing in a type-2 diabetes mouse model. In vivo wound healing in mice under a normal (Control Diet) or high fat diet was measured in the absence or presence of MSC or MSC-EC secretome. Images and total values of wound closure were shown at 2, 4, and 7 days post-injury. One-way ANOVA followed by a Tukey–Kramer test was used to examine the difference between experimental group. Values are expressed as mean, and S.E.M., n = 5. Statistical significance is represented as * p < 0.05 MSC-EC vs. MSC, *** p < 0.01 MSC-EC vs. PBS was considered significant.