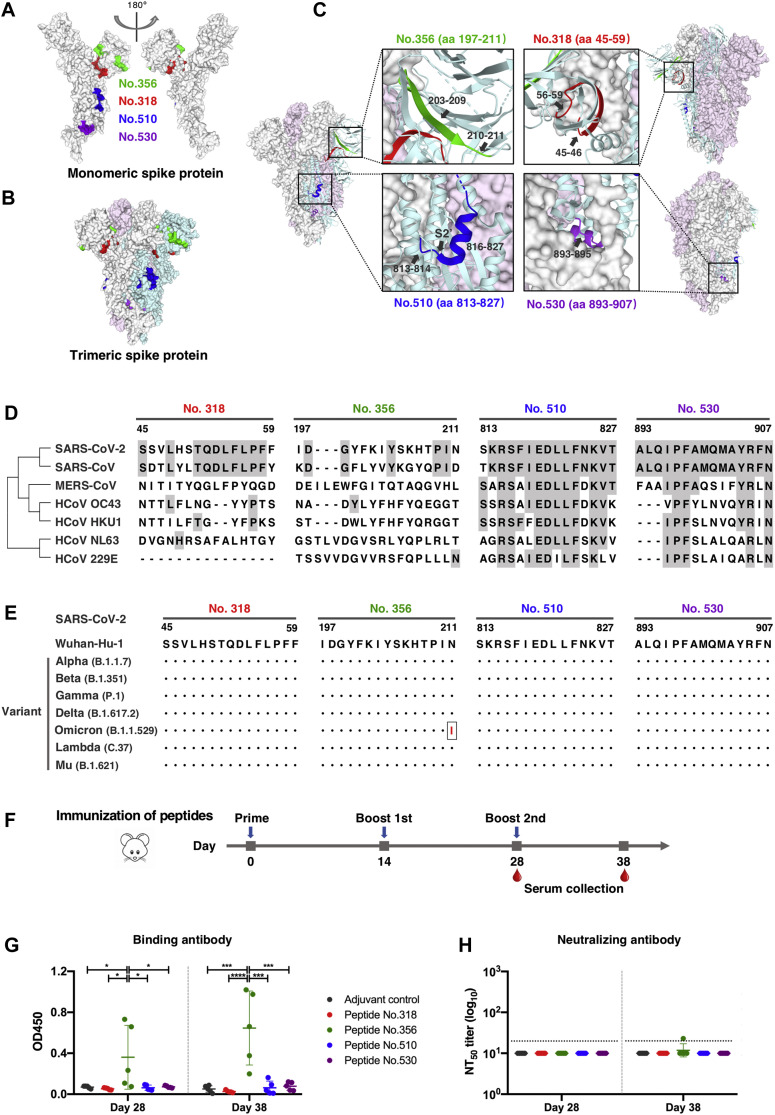
Fig 4.
Dominant epitopes of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein in terms of mediating durable humoral immune responses. A and B, Locations of the dominant and persistent epitopes on 3-D structures of the monomeric (A) and trimeric (B) S protein (PDB ID: 6VXX). Epitopes are highlighted in green (peptide 356, aa 197-211), red (peptide 318, aa 45-59), blue (peptide 510, aa 813-827), and purple (peptide 530, aa 893-907), respectively. The three S monomers in closed-conformation are depicted in gray, pink, and cyan, respectively. C, Detailed structure analysis of dominant epitopes in SARS-CoV-2 S protein on the closed state of the S trimer (PDB ID: 6VXX). D, Sequence alignment of identified epitopes among common human coronaviruses. Epitope residues that are conserved between SARS-CoV-2 and other human coronaviruses are shaded in gray.E, Epitope conservation analysis of the early SARS-CoV-2 (strain Wuhan-Hu-1) and 7 emerging variants. Black dots represent identical residues between the Wuhan-Hu-1 strain and the indicated variant. A single N211I substitution occurring in the Omicron variant is highlighted in red.F, BALB/c mice were immunized 3 times with each of the 4 selected S-protein peptides mixed with alum and CpG adjuvants. Sera were collected at day 14 after the second immunization and at day 10 after the third immunization. G, The levels of antigen-specific IgG antibody in immunized mouse sera (1:40 diluted) were tested by peptide-based ELISA. Statistical differences between groups were determined by 1-way ANOVA with Tukey multiple comparison. ∗P < .05, ∗∗∗P < .001, and ∗∗∗∗P < .0001. H, Neutralizing activity of mouse sera against pseudotyped SARS-CoV-2. Dotted horizontal lines indicate the lowest serum dilution in the assay (1:20).