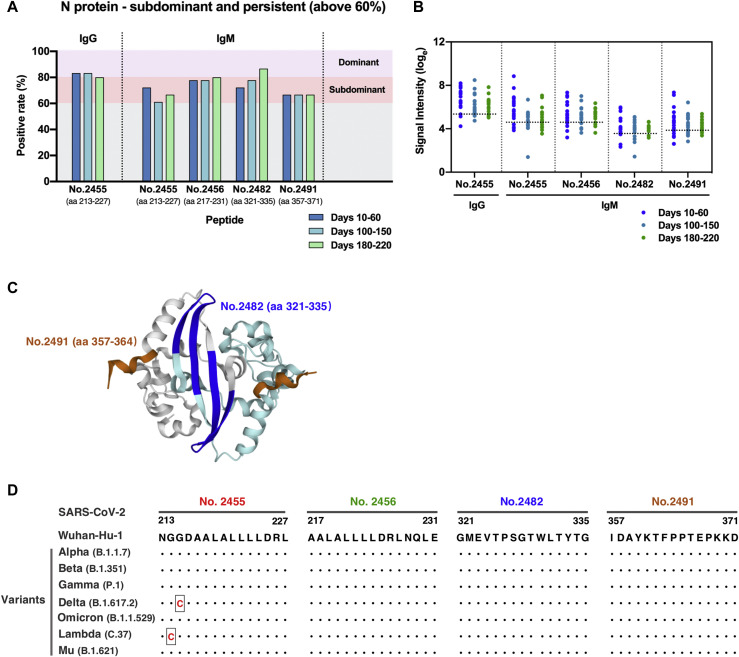
Fig 5.
Subdominant epitopes located at the SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein capable of mediating persistent antibody responses. A, IgG and IgM recognition frequencies of subdominant peptides (durably reactive in more than 60% samples) among patient serum samples collected at multiple time points after disease onset. B, Signal intensity kinetics of identified subdominant epitopes over time. Each dot represents a distinct patient serum sample obtained from COVID-19 patients at indicated time points after symptom onset. Dotted horizontal lines indicate cutoff values of positive response for each peptide. C, Detailed structure analysis of epitopes on the C-terminal dimerization domain of the N protein (PDB ID: 6YUN). Epitopes are labeled in blue (peptide 2482, aa 321-335) and brown (peptide 2491, aa 357-364). The 2 monomeric structures are depicted in gray and cyan, respectively. D, Sequence alignment analysis of the identified N-protein epitopes between the early SARS-CoV-2 (strain Wuhan-Hu-1) and 7 emerging variants. Black dots denote identical sequences between the Wuhan-Hu-1 strain and the indicated variant. Changes in amino acid sequence are highlighted in red.