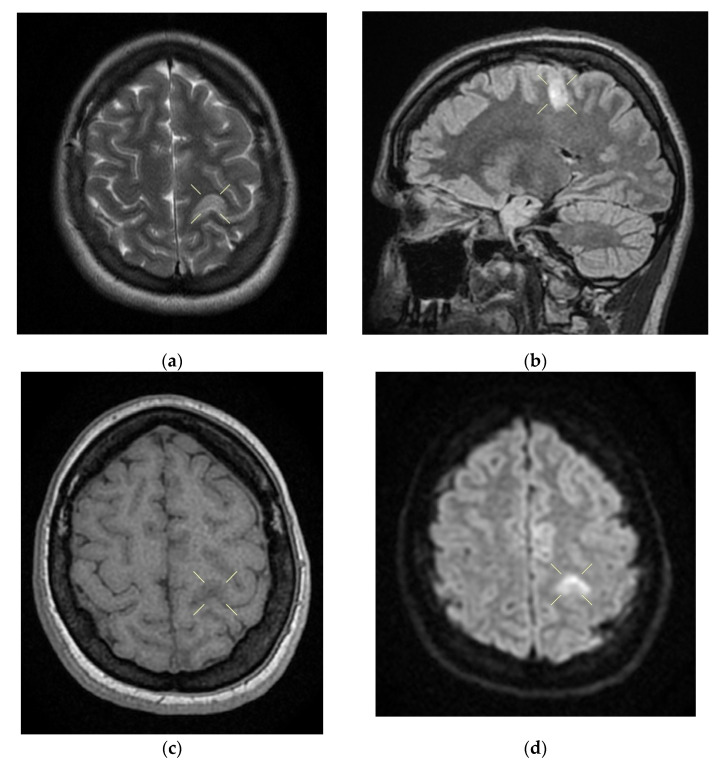
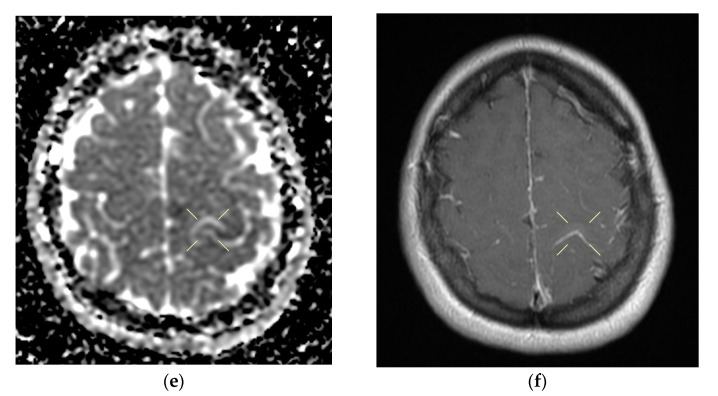
Figure 4.
Native and contrast-enhanced cerebral MRI and angiography with arterial and venous sequencing, performed on the second day of hospitalization. The scan indicates thrombosis of the left parietal cortical vein associated with ipsilateral superior parietal subcortical venous infarction—(a) band in T2 and FLAIR hypersignal. (b) band in T2 and FLAIR hypersignal. (c) T1 hyposignal. (d) restrictive in diffusion coefficient. (e) restrictive in diffusion coefficient. (f) restrictive in diffusion coefficient with weak contrast enhancement. Demyelinating lesions are organized in the crown, radiated and parietal on the right side, most probably with an ischemic vascular sublayer. The native cranio-cerebral and post-contrast MRI examination with arterial and venous angiographic sequencing highlighted the following: normal pericerebral liquid spaces; a symmetric ventricular system, with normal dimensions; an area in the hypersignal band T2, and a FLAIR/iso-hypo signal T1, with restricted diffusion weighing, weak gadolinophilia, axial dimensions of about 9/16 mm, located subcortically and parietally on the upper left side; two millimeter focal points of the T2 and FLAIR hypersignal, with no diffusion restrictions or detectable contrast outlet organized in the crown, radiated and parietal subcortical on the right side, in the area adjacent to the dorsal horn of the VL; structures of the median line in the right position; orbits and orbital content without anomalies; paranasal sinuses with normal development and pneumatization; the absence of images evoking hemorrhagic accumulations or masses with a tumor sublayer; symmetrically disposed internal carotid arteries with normal trajectories and caliber; a normal bilateral carotid siphon with no position or extrinsic compression anomalies, with homogeneous intensity of the intralumenal signal; anterior and middle cerebral arteries that were normally detached from the internal carotid on both sides, without any areas of inferior longitudinal stenosis with an aspect within the normal limits; transverse and symmetric sigmoid sinuses, without lesions; the rest of the patient’s evaluable venous segments did not present any defect in the lumen signal.