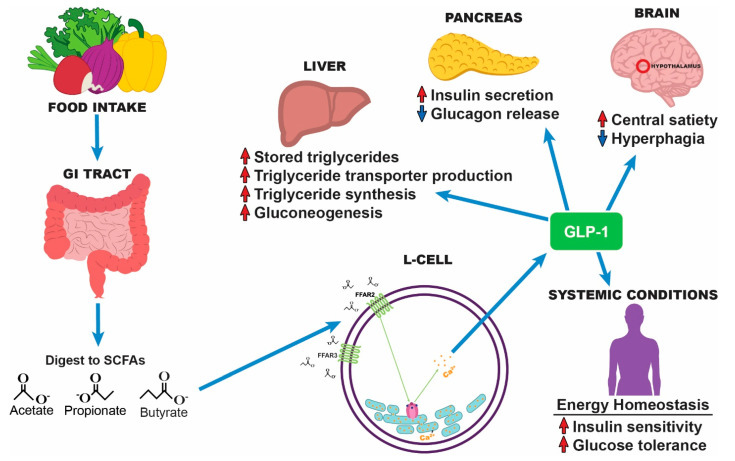
Figure 2.
SCFAs bring about system-wide improvements in ACVD risk factors via GLP-1. Following food intake, dietary fibers are digested by gut microbiota into SCFAs including acetate, propionate, and butyrate. These SCFAs activate intestinal L cells, leading to the release of GLP-1 both independently of and in conjunction with FFAR2 and FFAR3 activation. GLP-1 modulates a variety of organ functions including the liver, pancreas, and brain. It also systemically improves insulin sensitivity and glucose tolerance. This ability to improve various cardiovascular and metabolic risk factors for ACVD implicates GLP-1 and its synthetic mimetics as a viable treatment option for atherosclerosis.