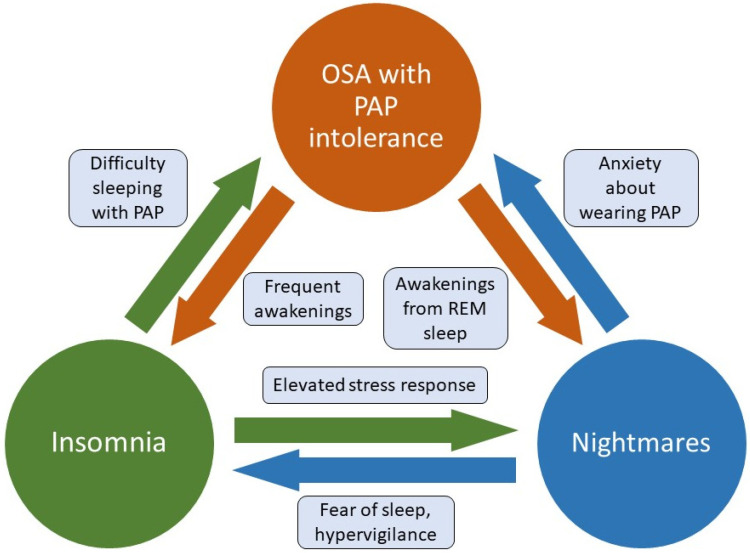
Figure 1.
Factors contributing to untreated OSA, insomnia, and nightmares in PTSD sufferers. Untreated sleep apnea may lead to frequent awakenings which precipitate and/or perpetuate insomnia, as well as arousals from REM sleep leading to increased nightmare intensity and recall. Difficulty initiating and maintaining sleep interferes with the ability to tolerate PAP therapy, and hyperarousal related to insomnia may increase nightmares via elevated stress response during REM sleep. The presence of nightmares often leads to fear of sleep, hypervigilance, and poor sleep hygiene (e.g., leaving lights on) that worsen insomnia. Nightmares may also reduce PAP tolerance due to increased anxiety and hypervigilance. OSA, obstructive sleep apnea. PAP, positive airway pressure. REM, rapid eye movement.