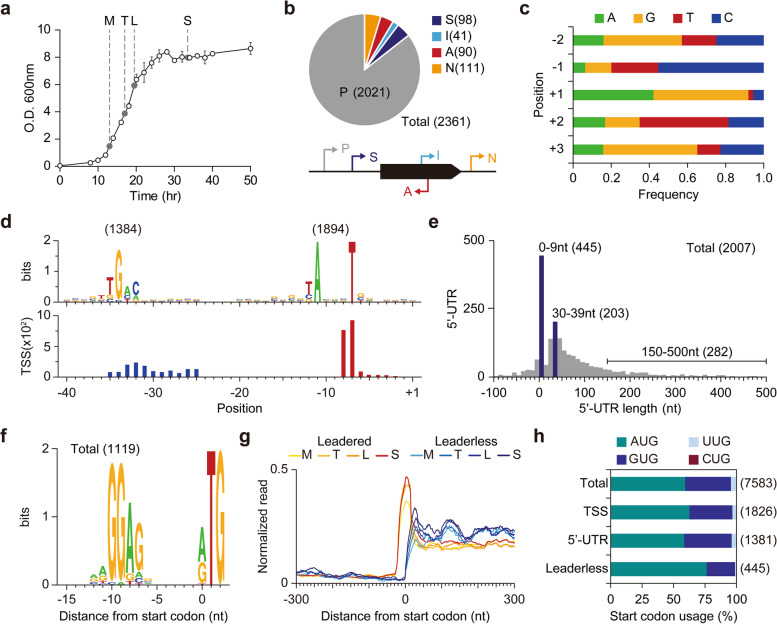
Fig. 1.
Genome-wide identification of transcription start sites. a Growth profile of S. avermitilis and sampling time points. Cells were harvested 13, 17, 19.5, and 33.5 h after inoculation for mid exponential, transition, late exponential, and stationary phases, respectively. b The number of transcription start sites (TSS) identified in this study. The identified TSSs were classified as either primary (P), secondary (S), internal (I), antisense (A), or intergenic (N) based on the relative position from adjacent genes. c Nucleotide frequency near TSSs. d Conserved promoter sequence of S. avermitilis. Each promoter motif was found separately using MEME suite. e The distribution of the 5′-UTR length. The 5′-UTR length was calculated as the distance from primary TSS to its associated CDS. f Conserved RBS sequence of S. avermitilis. RBS sequence was found with the whole sequences of 5′-UTRs longer than 10 nt. g Ribo-Seq read density near start codons of leaderless mRNA and leadered mRNA (h) Start codon usage of leaderless mRNA and other mRNA