FIGURE 1.
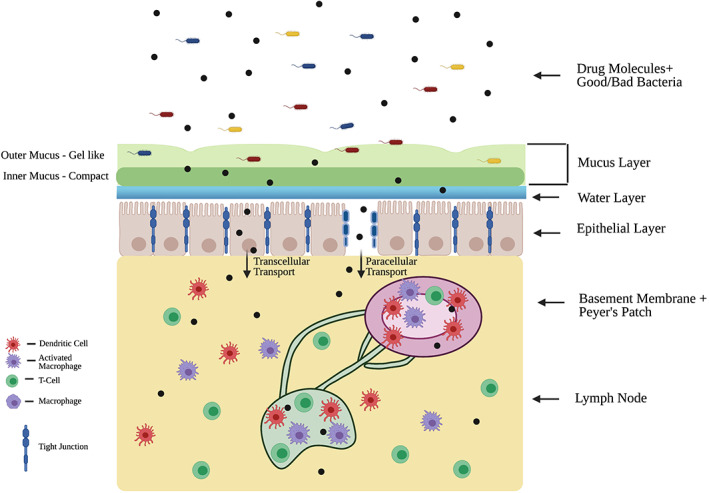
Drug molecules must bypass various barriers in the intestinal tract to reach systemic circulation. Some of these barriers include microbiota, mucosa, epithelial cells, and the immune system. Microbiota maintain immune homeostasis in the gut. A double‐layered mucosa coats the epithelium, which is bound by tight junctions. The basement membrane forms a dense layer under the epithelial layer. The gut barrier also houses several key immunological components (Peyer's patches, lymph nodes, dendritic cells, macrophages, T cells), which play an important role in preventing foreign pathogens/materials from invading systemic circulation
