Figure 3.
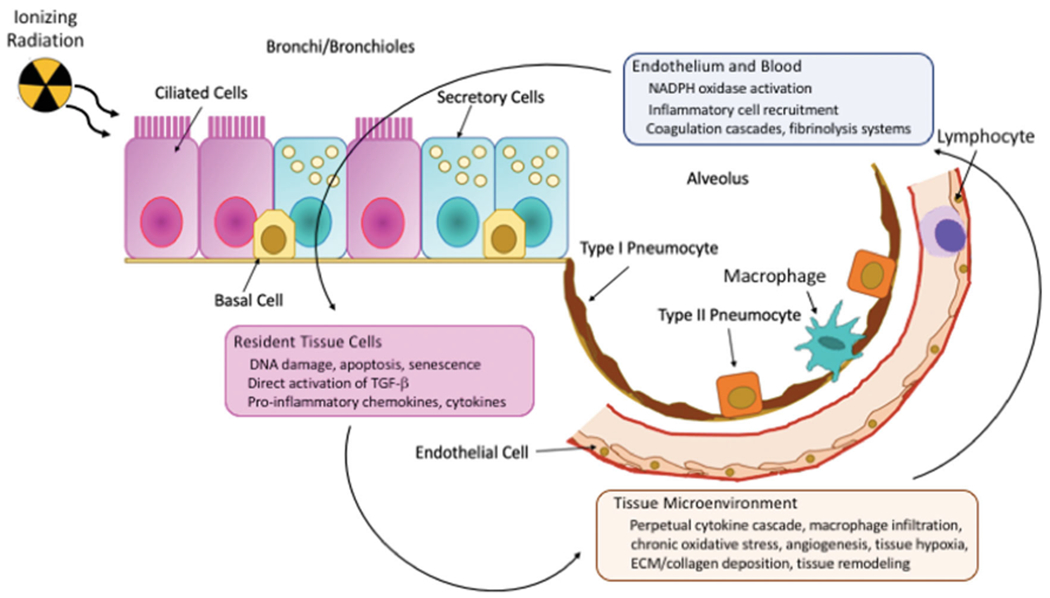
The development of radiation-induced lung injury is biologically complex. Of the 90+ cell types in the lung, there is no single target cell that initiates the response, although several are currently considered candidates. Progression to the early (pneumonitic) and late (fibrotic) phases involves multiple, parallel events, including initial and/or delayed hypoxia due to occlusion and permanent loss of blood vessels, respectively, waves of inflammatory cell recruitment and activation (including macrophages, lymphocytes and platelets), and chronic oxidative stress. Adapted from Bentzen 2006, Schaue et al. 2012 and Leiva-Juárez et al. 2018.
