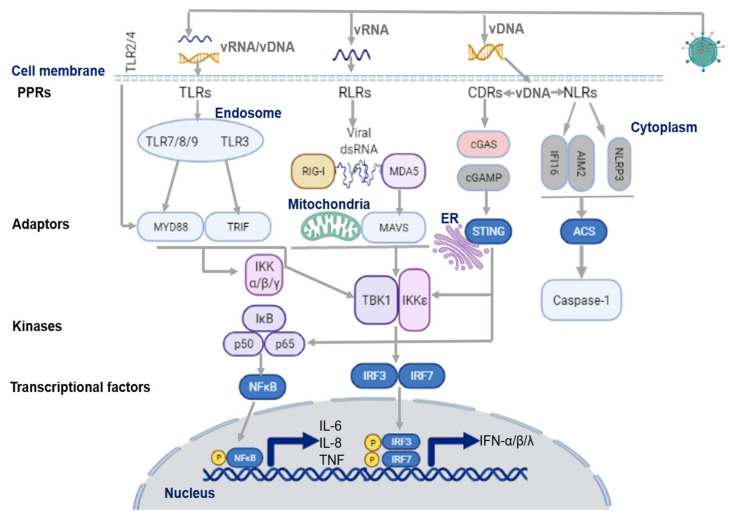
Figure 1.
Virus sensing pathways on airway epithelium. TLR7/8/9 and TLR3 in the endosome sense ssRNA, and dsRNA of the viral genome, respectively. They then activate their adaptor proteins, MyD88 for the former, and TRIF for the latter. The cell surface receptors, TLR2/4/6, also recognize respiratory viruses in the airway by modulating the adaptor protein, MyD88, to induce the antiviral response. DNA and RNA viruses release their genomes in the cytoplasm, where host innate sensors for viral RNA/DNA reside. Upon ss/dsRNA binding, RLRs interact with the adaptor protein, MAVS, on the mitochondrial outer membrane. CDRs (such as cGAS receptor) sense dsDNA and the RNA: DNA hybrids, and induce the synthesis of cGAMP, which then binds to the adaptor protein, STING. NLRs recognize DNA and RNA viruses via the NLRP3 inflammasome. NLRP3 activates and recruits ASC and procaspase-1 to form an inflammasome complex; IFI16 can recruit STING in response to cytoplasmic DNA through a molecular mechanism yet to be described. NLRs modulate the recruitment of their adaptor protein, ASC, to induce inflammation through the activation and secretion of pro-IL-1β and pro-IL-18 via caspase-1. The maturation of these cytokines further stimulates the production of IFNs and other cytokines. On the other hand, adaptor proteins, MyD88, STING, and MAVS, stimulate downstream signaling cascades that involve multiple kinases (TBK1, IKKs), and finally lead to IRF3/7 phosphorylation and nuclear translocation. The primary consequence of these virus-sensing pathways is the induction of type I/III IFN and pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines. ASC, adapter protein apoptosis-associated speck-like protein containing a caspase recruitment domain; CDR, cytosolic DNA receptors; cGAS, cyclic GMP-AMP synthase; cGAMP, 2′3′guanosine-adenosine monophosphate; IFI16, interferon-g inducible protein 16; IFN, interferon; IKK, IκB kinase; IRF3, interferon regulatory factor 3; MAVS, mitochondrial antiviral-signaling protein; MyD88, myeloid differentiation primary response 88; NLR, (NOD)-like receptor; NLRP3, NOD-, LRR- and pyrin domain-containing protein 3; RIG-I, retinoic acid inducible gene-I; RLR, RIG-1-like receptors; ss/dsRNA, single-stranded/double-stranded RNA; vRNA/DNA, viral RNA/DNA; STING, stimulator of interferon genes; TANK, TRAF-associated NF-κB activator; TBK1, TANK binding kinase 1; TLR, toll like receptor; TRIF, toll/IL-1R domain-containing adaptor-inducing IFN-β. Figure created with BioRender.com (accessed on 10 October 2021).