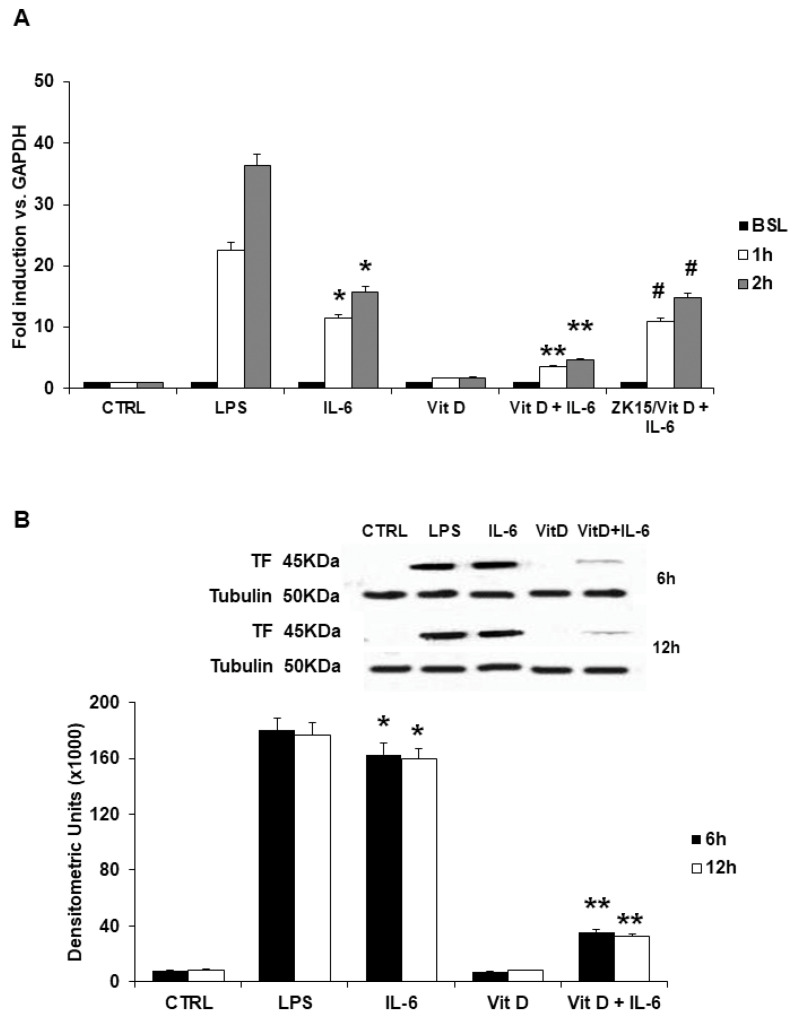
Figure 1.
(A) Effects of VitD on IL-6-induced TF transcription in human endothelial cells assessed by Real Time quantitative PCR. TF mRNA was undetectable at baseline. Incubation with IL-6 caused significant increase in TF-mRNA levels, as compared to unstimulated cells. Preincubation with VitD inhibited the IL-6 effect on TF-mRNA. The use of ZK15, a VDR antagonist, completely abolished its effect. LPS served as positive control. Data are expressed as fold induction versus control gene represented by GAPDH. Each bar represents the mean ± SD of 3 different experiments. (* p < 0.001 vs. Control; ** p < 0.001 vs. IL-6; # p = NS vs. IL-6; one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc test). (B) Effects of VitD on IL-6-induced TF protein evaluated by Western blot analysis of cell lysates. IL-6 caused a significant increase in TF protein levels. These effects were prevented by treatment with VitD. Tubulin served as loading control. LPS served as positive control. Each bar represents the mean ± SD of 6 different experiments (* p < 0.001 vs. Control; ** p < 0.001 vs. IL-6; one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc test). The insert shows results of a representative experiment.