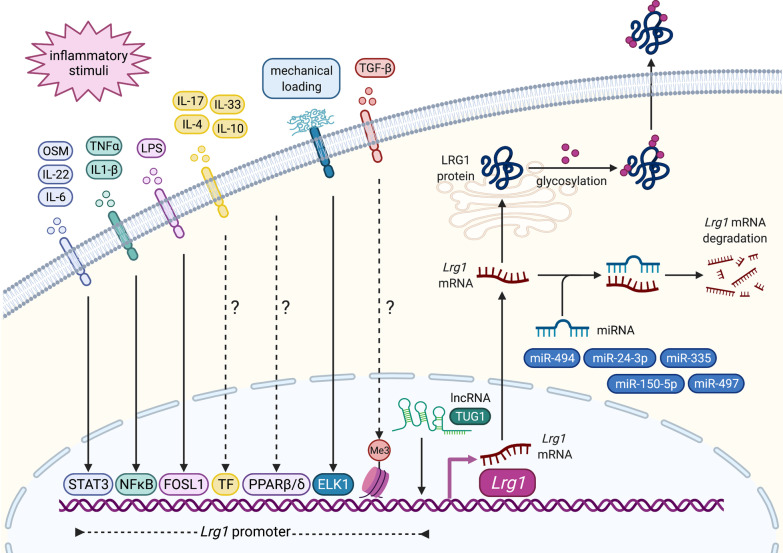
Fig. 4.
Regulation of Lrg1 expression. Schematic representation of the mechanisms regulating LRG1 expression at transcriptional and post-transcriptional levels. Several pro-inflammatory signalling molecules, including cytokines and bacteria-derived LPS, drive the expression of Lrg1 by promoting the activation of different transcription factors in a cell- and context-specific manner. Importantly, the combined stimulation with different cytokines has a synergistic effect on the activity of Lrg1 promoter. Biomechanical forces also stimulate Lrg1 expression through the FAK/ERK/ELK1 axis. Various non-coding RNAs have been associated with Lrg1 regulation. While the lncRNA TUG1 directly facilitates Lrg1 transcription, miR-335, miR-494, miR-497, miR-150-5p and miR-24-3p promote the degradation of Lrg1 mRNA and therefore are often downregulated in cancer. TGFβ-induced methylation has also been reported to favour expression of the Lrg1 gene. Finally, LRG1 protein is differentially glycosylated in a cell- and function-specific fashion prior to secretion into the extracellular space. OSM Osteopontin, lncRNA long non-coding RNA