Table 1.
Classification of PVBs morphology according to the probability of an underlying pathological myocardial substrate.
| QRS Morphology | Probable Origin of PVB | Disease Probability | V1 Pattern | aVF Pattern | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Common | |||||
| LBBB, late precordial transition (R/S = 1 after V3), inferior axis. | Right ventricular outflow tract. | Usually benign. |
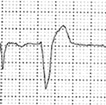
|
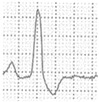
|
[8,61,62] |
| LBBB, inferior axis, small R waves in V1, early precordial transition (R/S = 1 by V2 or V3). | Left ventricular outflow tract. | Usually benign. |
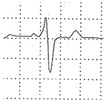
|
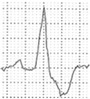
|
|
| QRS <130 ms resembling a typical RBBB/left anterior fascicular block. | Left posterior fascicle of the left bundle branch. | Usually benign. |
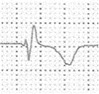
|
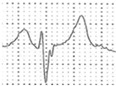
|
[63] |
| QRS <130 ms resembling a typical RBBB/left posterior fascicular block. | Left anterior fascicle of the left bundle branch. | Usually benign. |
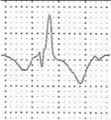
|
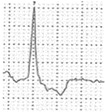
|
|
| Uncommon | |||||
| Atypical RBBB, QRS ≥130 ms, positive QRS in V1–V6 and inferior axis. | Anterior mitral anulus/left ventricular outflow tract. | Usually benign but may be associated with myocardial disease. |
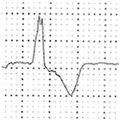
|
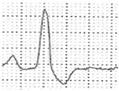
|
[64] |
| Atypical RBBB, QRS ≥130 ms, intermediate or superior axis. | Left ventricular free wall. | May be associated with myocardial disease. |
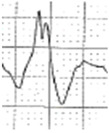
|
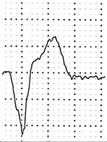
|
[65,66] |
| LBBB, superior or intermediate axis. | Right ventricular free wall or interventricular septum. | May be associated with myocardial disease. |
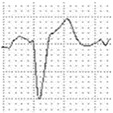
|
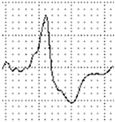
|
LBBB = left bundle branch block, i.e. negative QRS complex in V1; RBBB = right bundle branch block, i.e. positive or isodiphasic QRS complex in V1.
