Fig. 1.
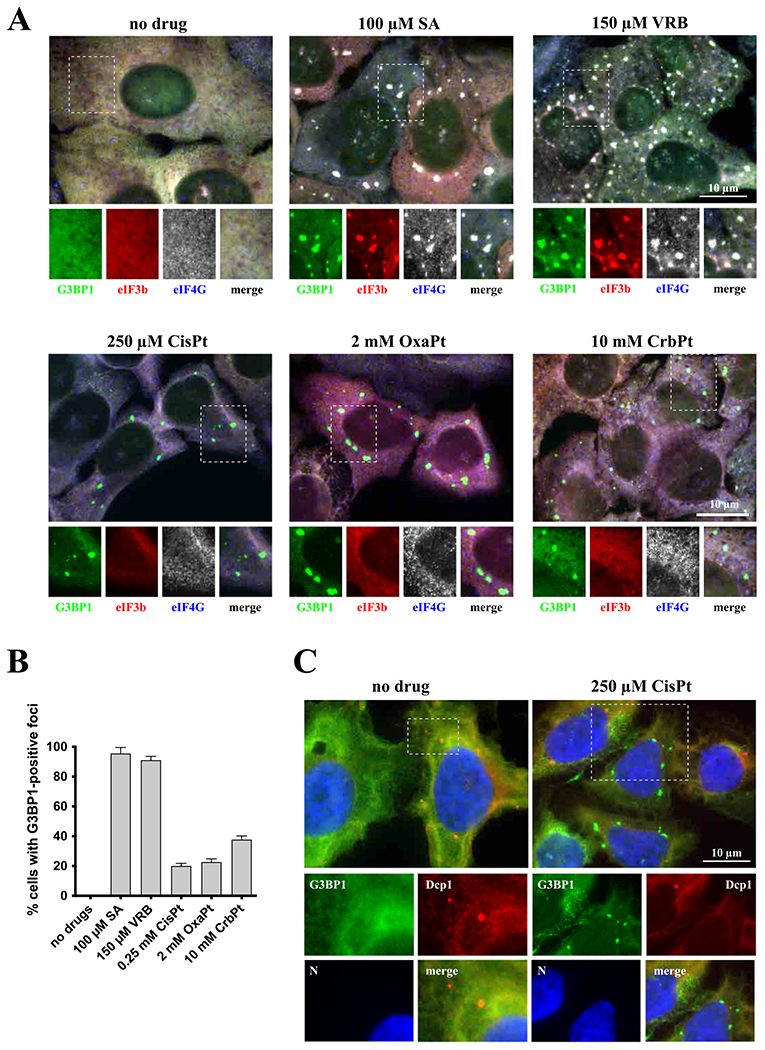
Platin-based drugs induce cytoplasmatic granules formation. (A) Formation of cytoplasmic granules. U2OS cells were stressed with sodium arsenite (SA, 100 μM) and vinorelbine (VRB, 150 μM) for 1 h, and with cisplatin (CisPt, 250 μM), oxaliplatin (OxaPt, 2 mM), and carboplatin (CrbPt, 10 mM) for 4 h. Unstressed U2OS cells were used as control (no drug). After treatment, cells were fixed and stained for stress granules markers: G3BP1 (green), eIF3b (red) and eIF4G (blue, shown as grey). Boxed region is shown enlarged with colors separated below each image. The size bar represents 10 μm. (B) Quantification of cytoplasmatic G3BP1-positive foci in U2OS cells (as shown in Fig. 1A). Data were analyzed using unpaired Student’s t-test, N = 3. (C) Detection of P-body marker Dcp1 in U2OS cells stressed with cisplatin (CisPt, 250 μM). Control, unstressed, population of U2OS cells was used as control (no drug). After treatment, cells were fixed and stained for G3BP1 (green), Dcp1 (red) and Hoechst (blue). Boxed region is shown enlarged with colors separated below each image; all colors (RGB) are merged in the main image. The size bar represents 10 μM.
