Figure 1.
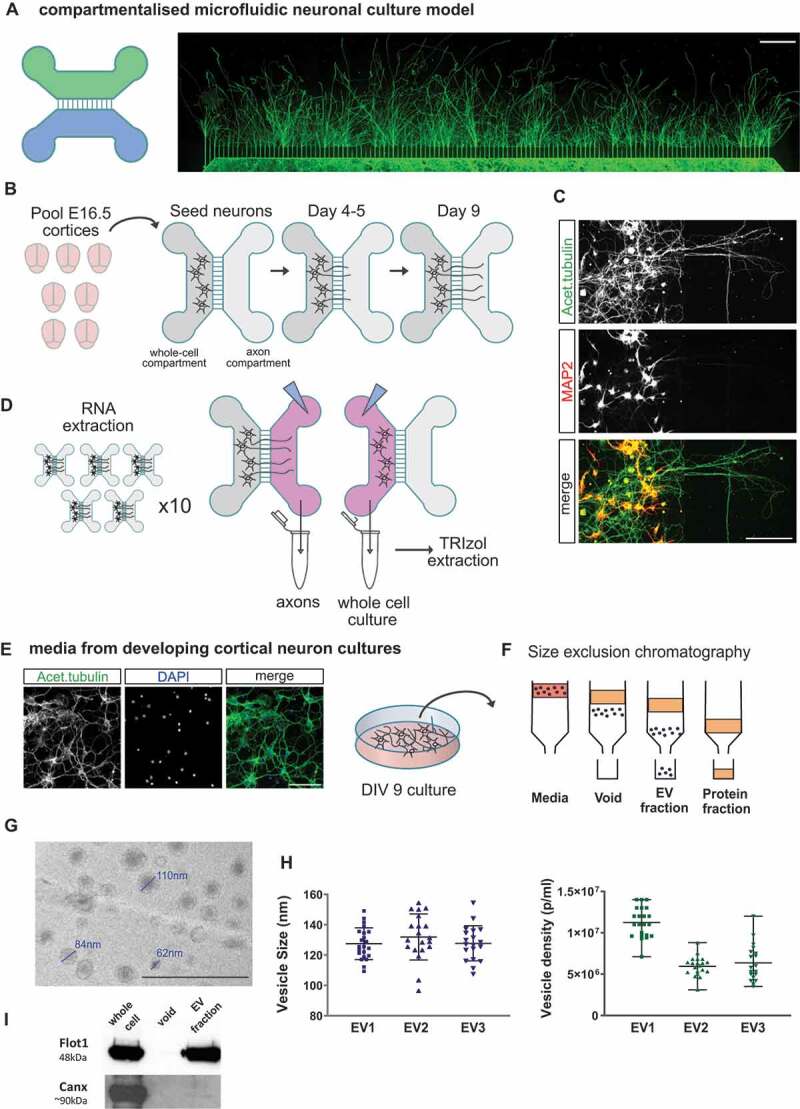
Primary cortical neuron culture models for RNA isolation from neuronal compartments: whole cell, axon and neuron-derived extracellular vesicles. (A) Schematic representation of a compartmentalized microfluidic chamber and immunofluorescence image of cortical primary neurons grown in this device. In this model two culture channels are connected by 150um microgrooves allowing compartmentalization of axons from their neuron cell bodies and dendrites. Acetylated tubulin staining (green) shows the presence of axons across the full axonal compartment at day 9 in culture (scale bar 500 µm). (B) Diagrammatic representation of the experimental preparation protocol using compartmentalized cultures. Post-mitotic cortical neurons are prepared from a E16.5 litter (total of ~7-9 cortices) and seeded onto the designated WC (whole cell) channel. As the culture develops, axons extend across the microgrooves and into the axonal channel at ~4-5 days in culture. WC and pure axonal fractions are harvested for RNA extraction at day 9 in culture to allow for extensive axon coverage in the axon channel. (C) Immunofluorescence image of cortical neurons in a microfluidic chamber and labelled with the dendritic marker MAP2 (red), which indicates how dendrites do not extend to the designated axonal (AX) side of the device at this stage in culture. On the other hand, the axon-enriched marker acetylated tubulin (green) is present in both WC and AX channels (scale bar 150 µm). (D) The WC and AX fractions of 40–50 microfluidic devices were collected and pooled for each biological replicate. To collect axonal pure fractions, TRIzol reagent was applied to the axonal channel whilst maintaining hydrostatic pressure in the WC channel with PBS, thus preventing contamination from the WC side. WC was collected immediately thereafter. (E) Neuron-derived extracellular vesicles (EV) were obtained from media collected from day 9 of standard primary cortical cultures as depicted (green: acetylated tubulin; blue: dapi; scale bar 100 µm). (F) Diagrammatic representation of the size exclusion chromatography method for the isolation of the EV fraction from neuronal culture media, highlighting how EVs are separated from the media’s protein fraction. (G) EV fractions were visualized by transmission electron microscope revealing the expected vesicular structure (scale bar 500 nm). (H) Nanoparticle tracking analysis (NTA) showing average particle size and mean particle density measured for the three EV preparations used for RNA extraction and small RNA-sequencing. Data expressed as mean ± range of NTA measurements. (I) Western blotting of the isolated EV fraction showing the presence of EV marker flotilin-1 (Flot1) and near absence of calnexin (Canx), an endoplasmatic reticulum marker largely absent in small EVs (< 200 nm).
