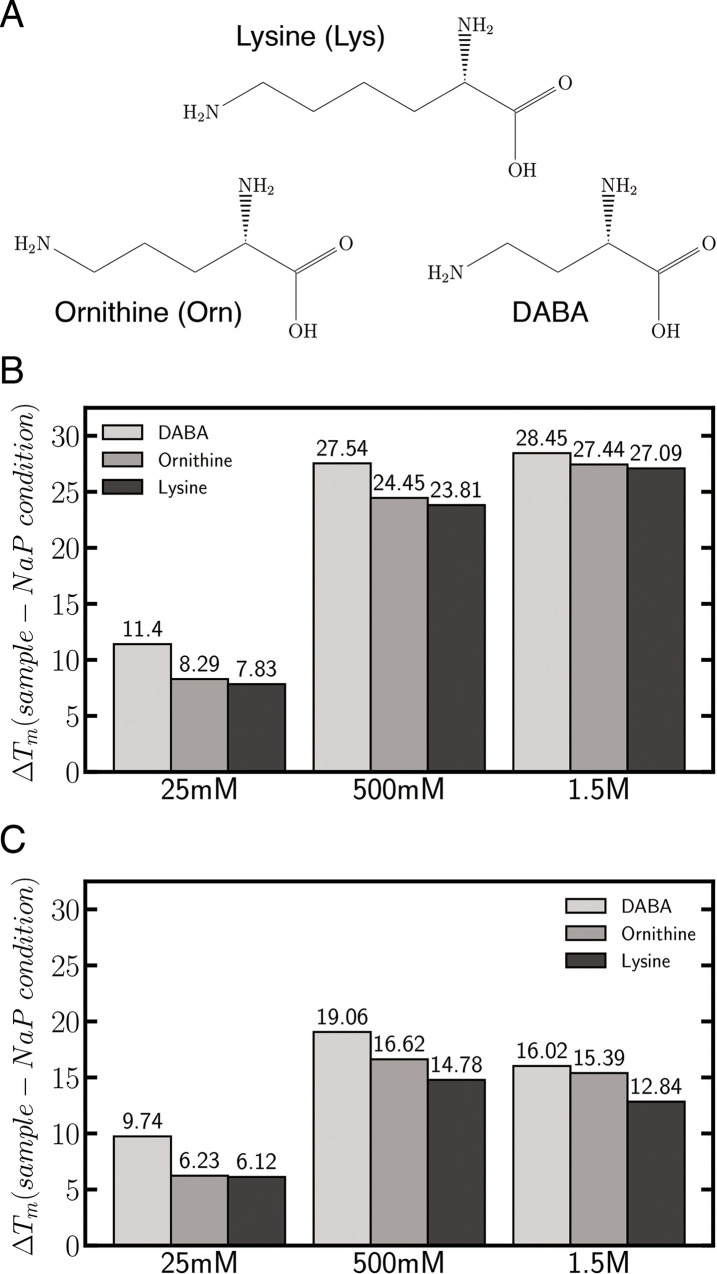
Fig 2. Lysine and derivatives stabilize AT- vs GC-rich DNA duplexes differentially depending in the length of their carbonated side chain.
A) Scheme of Lysine and Lys-derivative structures. B) Melting temperatures relative to NaP buffer (ΔTm) of AT-rich duplexes in the presence of Lysine and Lys-derivatives. C) Melting temperatures relative to NaP buffer (ΔTm) for GC-rich duplexes in the presence of Lysine and Lys-derivatives (average between two replicas—std < 3% of the average for all samples).