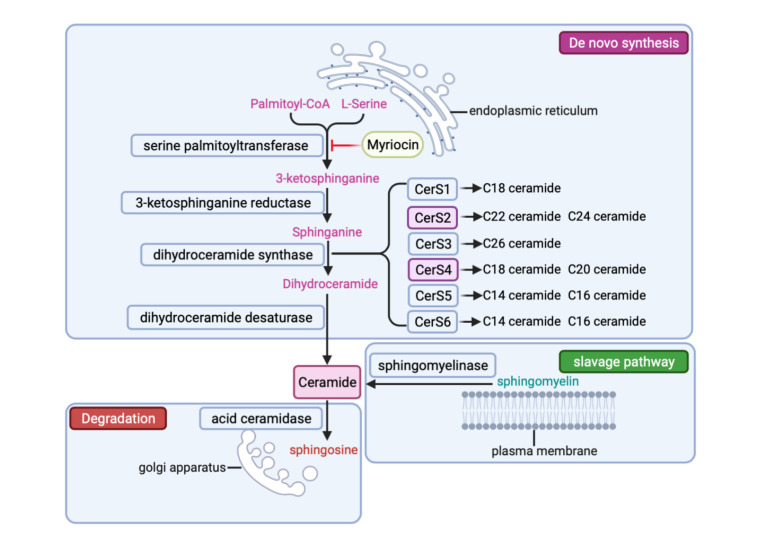
Figure 1.
The metabolic pathway of ceramide. De novo synthesis (purple) takes place in the endoplasmic reticulum, L-serine and Palmitoyl-CoA are catalyzed by serine palmitoyltransferase (which has a specific inhibitor-Myriocin) to produce 3-Ketosphinganine, which is then converted to sphinganine by 3-Ketosphinganine reductase. Six kinds of CerSs (CerS4 and CerS2 dominates in cardiomyocyte) then further synthesize the sphinganine into dihydroceramide, which are then reduced by dihydroceramide desaturase to produce ceramides of different acyl chain lengths. Ceramide can also be generated through the slave pathway (green) on the cell membrane or be transported to the Golgi apparatus and degraded by acid ceramide into sphingosine.