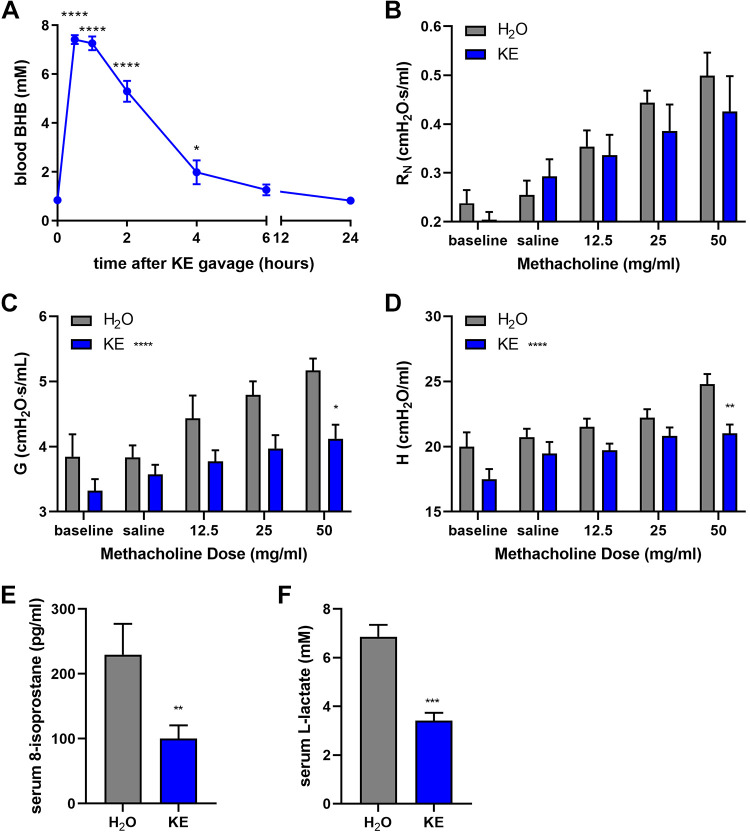
Figure 4.
Ketone ester administration acutely decreases methacholine responsiveness. Mice were administered 200 μL of water (H2O) or ketone ester (KE; ∼4 g/kg) by oral gavage. Blood β-hydroxybutyrate (BHB) (A) was measured before or at several time points following KE administration; n = 5 mice/group. Airway resistance (RN) (B), tissue damping (G) (C), and tissue elastance (H) (C) were measured 1 h following water or ketone ester gavage. Serum 8-isoprostane (E) and lactate (F) were measured; n = 6 mice/group. *P ≤ 0.05, **P ≤ 0.01, ***P ≤ 0.001, ****P ≤ 0.0001, compared with time 0 by ANOVA (A) or the water group by t test (E and F). *P ≤ 0.05, **P ≤ 0.01, compared with water group at the same dose of methacholine (B–D).