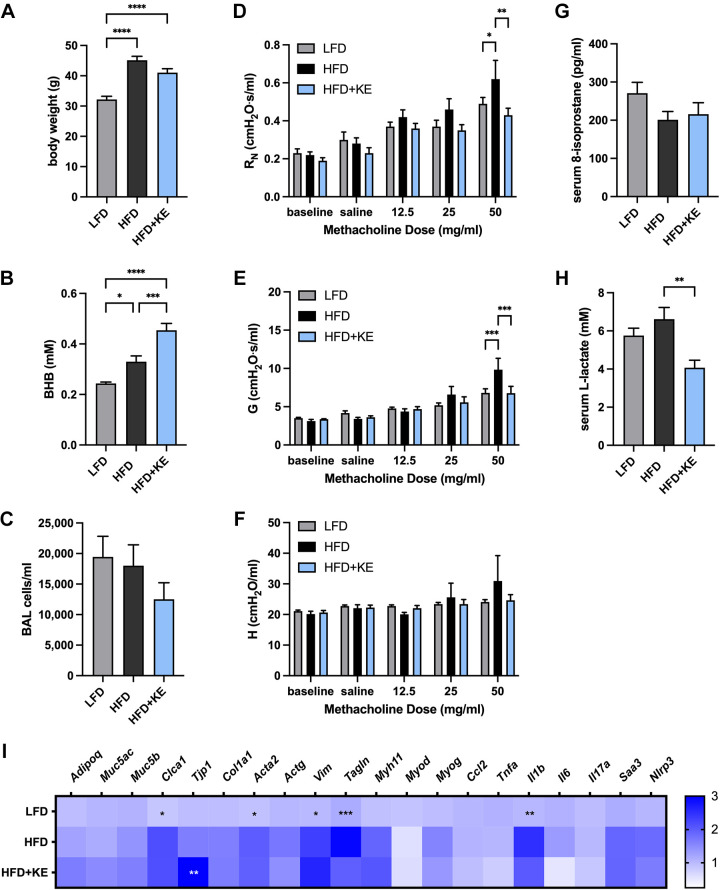
Figure 5.
Ketone ester supplementation decreases methacholine hyperresponsiveness in high-fat diet-induced obese mice. Mice were maintained on a low-fat diet (LFD), a high-fat diet (HFD), or a high-fat diet containing 20% (by weight) ketone ester (HFD + KE) for 3 wk. Body weight (A), serum β-hydroxybutyrate (BHB) (B), and total bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) cells (C) were measured. Airway resistance (RN) (D), tissue damping (G) (E), and tissue elastance (H) (F) were measured. Serum 8-isoprostane (G), serum lactate (H), and lung gene expression were measured and presented as expression relative to the mean of the LFD group, scaling from 0 to 3 (I); n = 8–10 mice/group.. *P ≤ 0.05, **P ≤ 0.01, ***P ≤ 0.001, ****P ≤ 0.0001, compared with indicated group (A–H) or HFD group (I).