Figure 6.
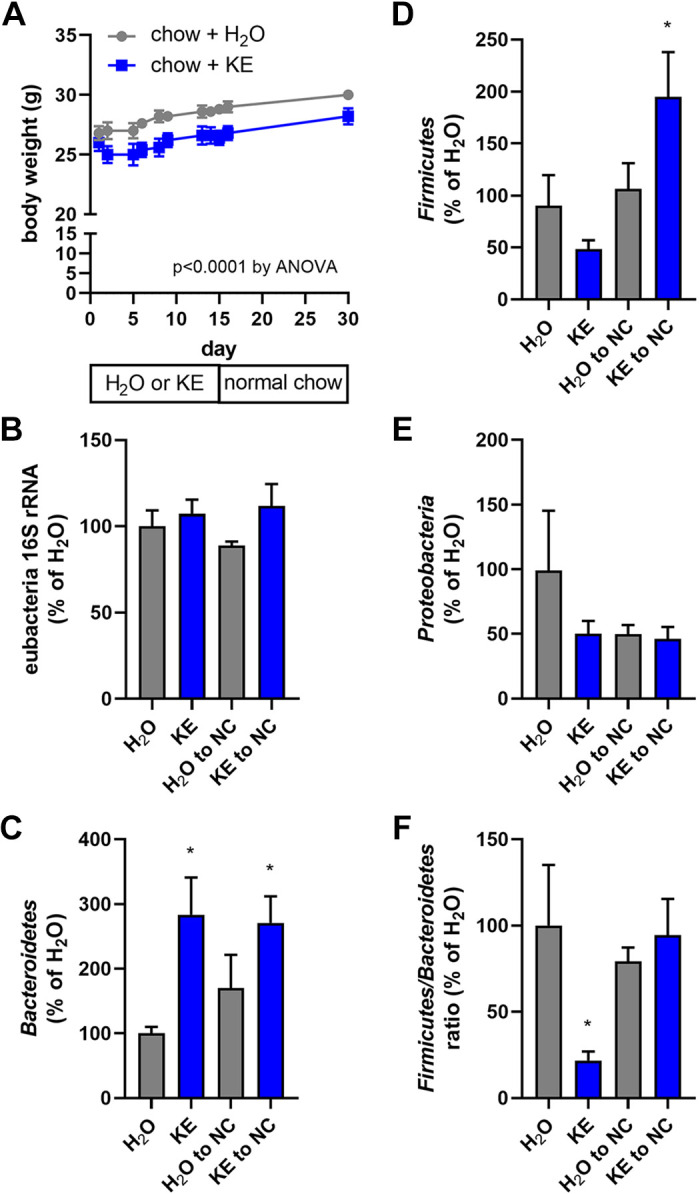
Ketone ester feeding promotes a transient anti-obesogenic gut microbiome. Mice were maintained on normal chow until day 0 and then maintained on chow containing 20% (by weight) water (H2O) or 20% ketone ester (KE) for 15 days and then switched back to normal chow (NC) until day 30. Body weight was measured on several occasions throughout the 30-day feeding regimen (A). Fecal pellet total eubacterial 16S rRNA (B) and phlya-specific 16S rRNA for Bacteroidetes (C), Firmicutes (D), and Proteobacteria (E) DNA content was quantitated on days 15 and 30, and expressed relative to that found in the chow + H2O fed mice at day 15. The Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes ratio, relative to that found in the chow + H2O fed mice at day 15, was calculated (F); n = 5 mice/group. *P ≤ 0.05, compared with indicated group.
