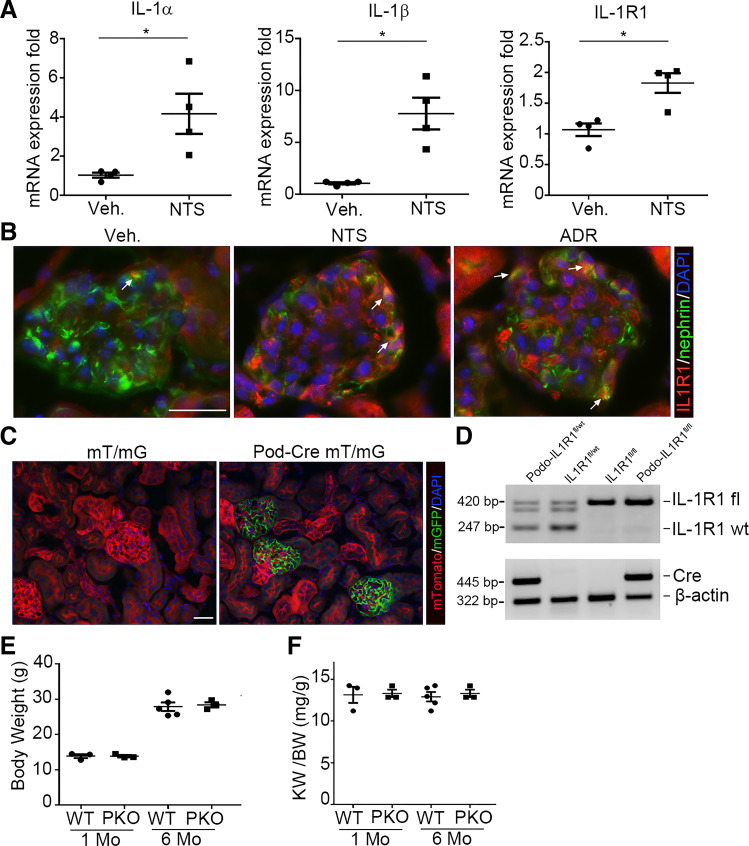
Figure 1.
Induction of interleukin (IL)-1 signaling components in glomeruli from mice after glomerular injury. A: glomerular IL-1α, IL-1β, and IL-1 receptor type 1 (IL-1R1) mRNA abundance at day 9 after nephrotoxic serum (NTS)-induced glomerular injury (n = 4). B: representative IL-1R1- and nephrin-stained kidney sections from vehicle (Veh), NTS-, and adriamycin (ADR)-injected animals. The white arrows indicate the colocalization of IL-1R1 and nephrin in glomeruli. C: representative sections of kidneys from podocin (Pod) Cre− mT/mG and Pod Cre+ mT/mG reporter mice. Green fluorescence indicates the presence of podocin Cre expression; red fluorescence marks the absence of podocin Cre expression. Blue fluorescence indicates nuclear DAPI stain. D: genotyping of the mice by PCR analysis of genomic DNA. E and F: body weights (E) and kidney-to-body weight ratios (KW/BW; F) of naïve podocyte-specific knockout (PKO) and wild-type (WT) mice at 1 and 6 mo (n = 3–5). Data are presented as means ± SE. P values in A were analyzed by a two-tailed Student’s t test. *P < 0.05. Scale bars = 40 µm.