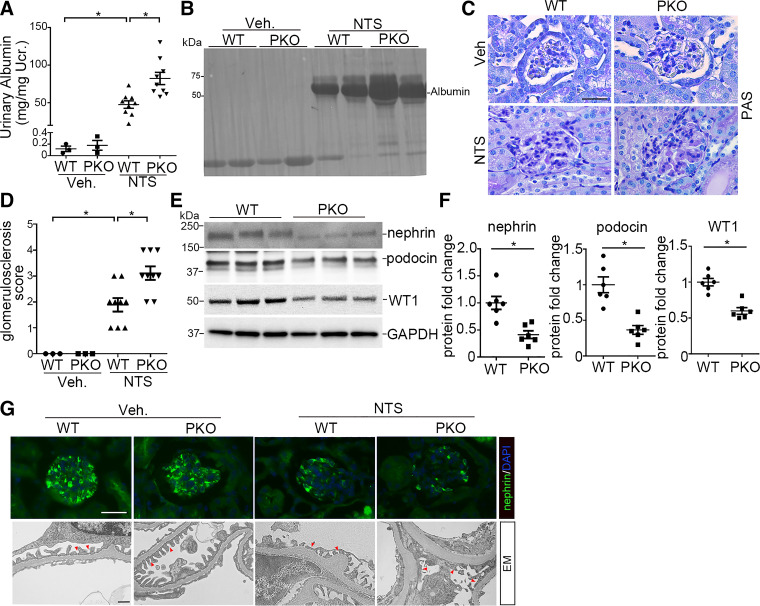
Figure 2.
Interleukin-1 receptor type 1 (IL-1R1) signaling in podocytes limits albuminuria and podocyte injury induced by nephrotoxic serum (NTS) in mice. A: urinary albumin concentration in wild-type (WT) and podocyte-specific knockout (PKO) mice at day 9 after vehicle (Veh) or NTS injection (n = 3–9). B: representative SDS-PAGE showing urine proteins in cohorts of mice. C: representative images of kidney sections from WT and PKO mice at day 9 after Veh or NTS injection. Scale bar = 40 µm. D: kidney glomerulosclerosis score in groups as indicated (n = 3–9). E: representative Western blots for nephrin, podocin, and Wilms’ tumor-1 (WT1) protein in glomeruli isolated from WT and PKO mice at day 9 after NTS. F: semiquantitative determination of nephrin, podocin, and WT1 protein from the blots shown in E (n = 6). G: representative immunostaining for nephrin protein and electron microscopy (EM) showing the glomerular filtration barrier in different groups. The red arrowheads indicate the secondary foot process and slit diaphragm. Scale bars = 40 µm (top) and 1 µm (bottom). Data are presented as means ± SE. P values in A and D were analyzed by a one-way ANOVA test followed by a Student–Newman–Keuls or Kruskal–Wallis test. P values in F were analyzed by a two-tailed Student’s t test. *P < 0.05. PAS, periodic acid-Schiff stain; Ucr, urinary creatinine.