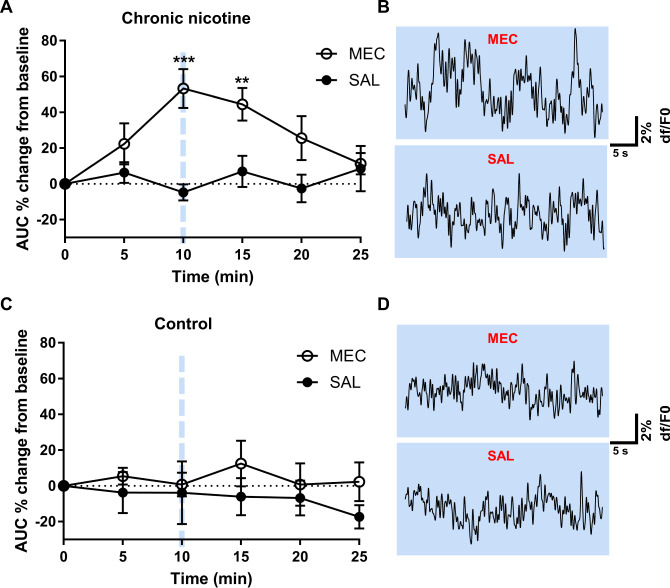
Fig. 2. Mecamylamine increases GCaMP activity from chronic nicotine but not vehicle control mice.
Analysis of the effects of mecamylamine and saline injections on GCaMP activity in chronic nicotine and control mice. A In chronic nicotine-treated mice, mecamylamine (1 mg/kg) significantly increased the AUC of GCaMP recordings at 10 and 15 min post injection compared to baseline (two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s post-tests). Representative GCaMP recordings taken 10 min post mecamylamine (top) and saline (bottom) injection are shown in (B). No significant differences in the AUC of GCaMP traces were observed in vehicle control mice following mecamylamine or saline injection (C). Representative traces for mecamylamine (top) and saline (bottom) from control mice are shown in (D). MEC mecamylamine, SAL saline.