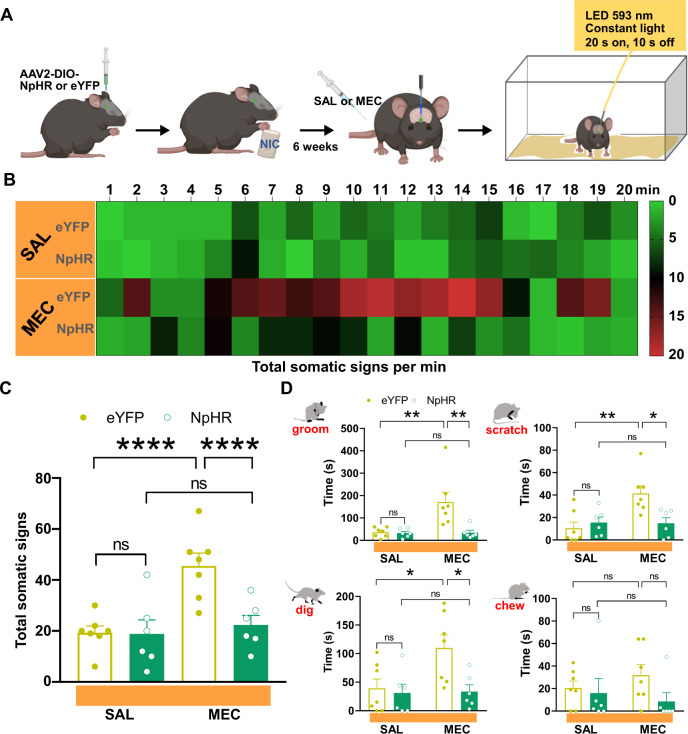
Fig. 4. Physical signs of nicotine withdrawal are inhibited by optical silencing of IPN GAD2+ neurons.
A Experimental design for optical silencing of IPN GAD2+ neurons. AAV2 Cre-dependent NpHR or eYFP were injected into the IPN of GAD2:Cre mice. Following 6 weeks of chronic nicotine drinking and implantation of optic fibers, mice were challenged with mecamylamine or saline in the presence of yellow light (593 nm, 20 s on, 10 s off) delivered into the IPN. Following injections, mice were immediately returned to their home cage and somatic behaviors were tallied for 20 min starting 2 min post injection. Time course of somatic events per min under each condition is shown in the heatmap in (B). Heatmap legend indicates number of somatic events. C In eYFP-expressing mice, mecamylamine induced a significant increase in somatic behavioral events as compared to saline, while no difference in total somatic behavior was observed following mecamylamine challenge compared to saline in NpHR-expressing mice (two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s post-tests). Total somatic event time was also calculated for each behavior investigated in photometry experiments and was compared across groups and treatment conditions. D Significant increases in time spent grooming, scratching, and digging were observed following mecamylamine injection as compared to saline in eYFP mice, but not NpHR-expressing mice (two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s post-tests). No difference in chewing time was observed across groups or treatment conditions (two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s post-tests). MEC mecamylamine, SAL saline.