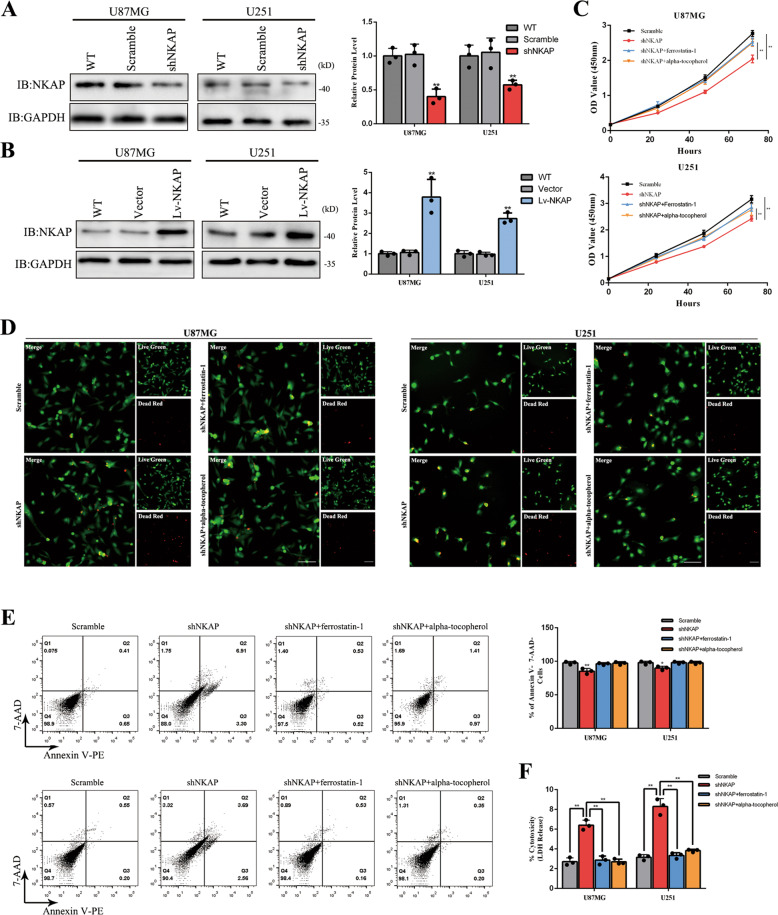
Fig. 1. NKAP knockdown caused an increased percentage of cell death in glioblastoma cell lines.
A The interference effect of shNKAP in U87MG and U251 cell lines. GAPDH was used as a loading control. B Protein overexpression level induced by Lv-NKAP in glioblastoma cell lines. GAPDH was used as a loading control. C The growth curves of the U87MG and U251 cells were examined using a CCK-8 assay. Cell growth was inhibited by NKAP knockdown and partially reversed by 0.5 μM ferrostatin-1 or 5 μM alpha-tocopherol for 24 h. D Live (green)/dead (red) staining revealed a higher cell death rate in the shNKAP group, which could be reversed by 0.5 μM ferrostatin-1 or 5 μM alpha-tocopherol for 24 h. Scale bar = 100 μm. E Cell death induced by NKAP knockdown in the absence or presence of 0.5 μM ferrostatin-1 or 5 μM alpha-tocopherol for 24 h detected by flow cytometry in U87MG and U251 cell lines. F LDH release induced by NKAP knockdown in the absence or presence of 0.5 μM ferrostatin-1 or 5 μM alpha-tocopherol for 24 h. All bars show the mean ± SD of three independent experiments. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01.