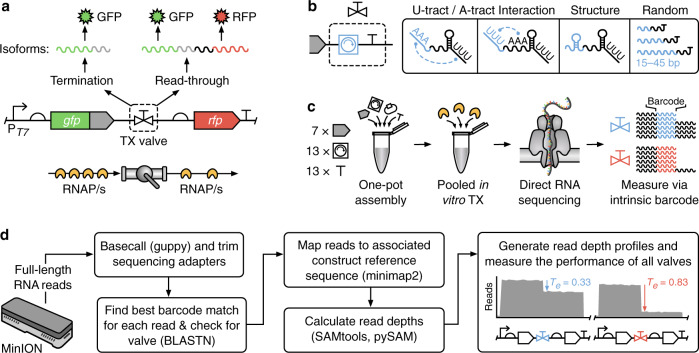
Fig. 1. Massively parallel characterization of transcript isoforms using nanopore-based direct RNA sequencing.
a Schematic of the genetic construct used to characterize transcriptional valves. A transcriptional valve controls the ratio of RNA polymerase (RNAP) termination to read-through and thus the proportions of transcript isoforms produced. b Our modular transcriptional valves comprise a ‘core terminator’ and ‘modifier’ sequence (blue) used to tune termination efficiency. Various modifiers were considered to interact with the U- and A-tract of the core terminator, form small secondary structures in the RNA, and act as different length inert spacing elements. c The steps involved in the assembly of the modular transcriptional valve library and its pooled characterization using nanopore-based direct RNA sequencing. d Analysis pipeline used to generate valve-specific read depth profiles and calculate termination efficiencies (Te) from pooled direct RNA sequencing data. Key computational tools are shown in parentheses.