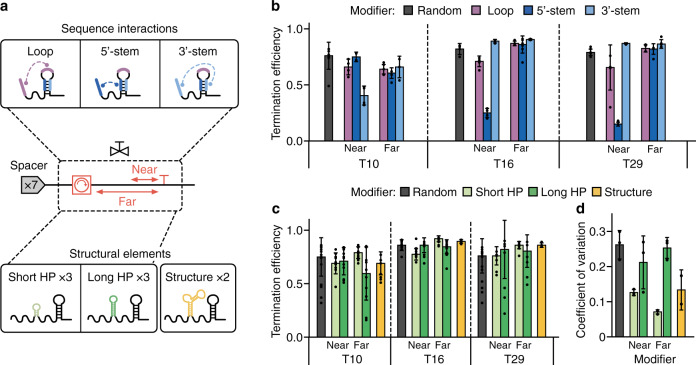
Fig. 4. Engineering modifiers that tune and insulate core terminators.
a Overview of the modifier library based on sequence interactions and structural elements used to explore tuning and insulation of core terminator function. A ‘near’ and ‘far’ modifier variant was designed for each motif (except for the random and structure options). Modifiers were designed to interact with the core terminator via sequence (upper) or structure (lower). For sequence interactions, 8 nt sequences were designed to be complementary to regions of the core terminator covering the loop (purple), 5′-stem (dark blue), 3′-stem (light blue). For structural elements, 3 short hairpins (light green), 3 long hairpins (dark green) and 2 further RNA structures (orange) were designed. b Termination efficiency (Te) for each valve designed to interact via sequence, grouped by modifier. Bars denote median Te values ± standard deviation (SD) and from left–right n = 6, 4, 2, 4, 5, 4, 3, 5, 4, 4, 3, 3, 6, 2, 7, 4, 3, 3, 4, 4 and 4. c Te for each designed structural element. Bars denote median Te values ± SD and from left–right n = 9, 10, 13, 12, 10, 17, 6, 14, 11, 9, 12, 14, 3, 8, 11, 8, 7 and 17. d Coefficient of variation of Te values for the structural elements. CV is calculated across spacers for each terminator and grouped by structural element. Bars denote mean CV values ± SD and from left–right n = 3, 3, 3, 3, 3 and 2. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.