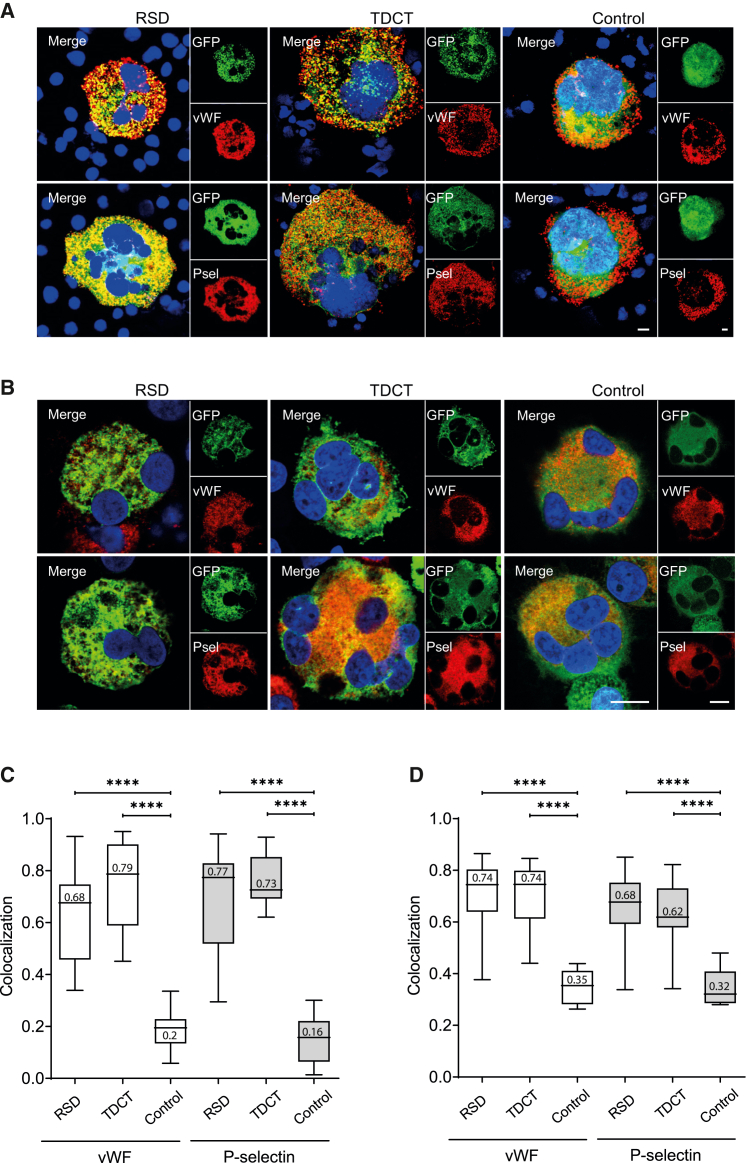
Figure 3.
Colocalization analysis of αG targeting in murine and human primary megakaryocytes (MKs)
Immunofluorescence images of MKs differentiated from transduced (A) murine lineage-marker-negative BM cells or (B) human CD34+ HSPCs. MKs transduced with RSD, TDCT, or control vector (green) were stained with antibodies against αG proteins (red) and DAPI (blue). vWF+ αGs were visualized with 1° rabbit antibodies (Abs) and 2° goat-anti-rabbit Alexa Fluor 647 Abs, while P-selectin+ αGs were visualized with 1° human/mouse Abs and 2° goat-anti-mouse Cy3 Abs. Images were acquired with a Zeiss confocal microscope and a 100× oil immersion objective for murine MKs or a Leica confocal microscope with a 63× oil immersion objective for human MKs. The merged images show colocalization of vector and αG protein; scale bar, 10 μm. Quantification of colocalization of GFP in the three vectors with vWF or P-selectin in (C) murine MKs (n = 11–28) and (D) human MKs (n = 8–28). MKs were analyzed from two (mouse) and three (human) independent transductions and differentiations. Line at median on box-whisker plots, Mann-Whitney test, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001.