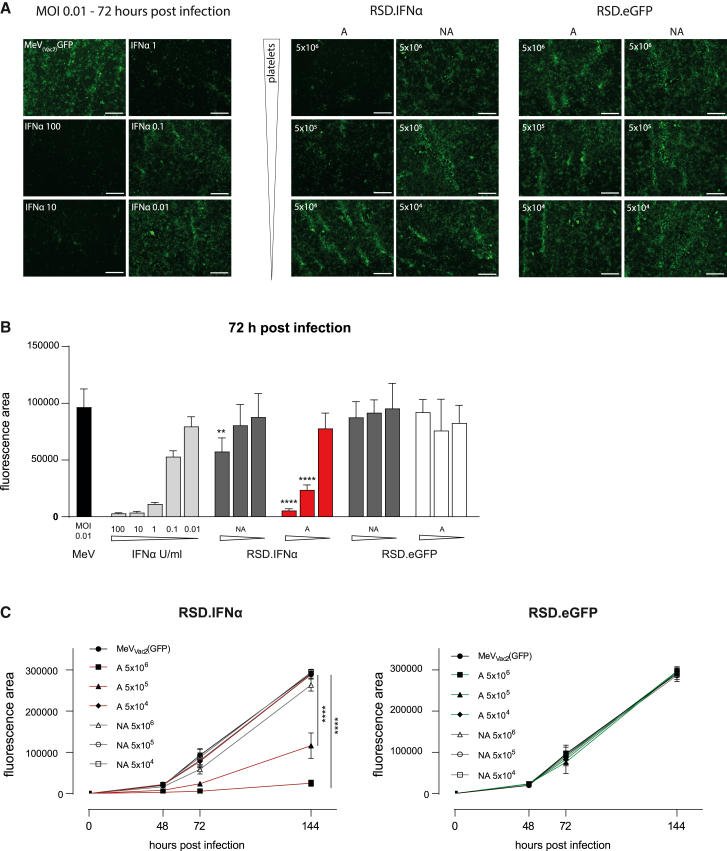
Figure 6.
Inhibition of virus replication by IFNα released from engineered platelets
(A) Left: fluorescence images of Vero-E6 cells infected with MeVvac2(GFP) at MOI 0.01 at 72 h after infection (left top image) and Vero-E6 cells infected and treated with decreasing doses of IFNα (100–0.01 U). Right: Vero-E6 cells infected with MeVvac2(GFP) at MOI 0.01 and treated with 5 × 106, 5 × 105, and 5 × 104 A or NA platelets from RSD.IFNα or RSD.GFP mice. Images were taken 72 h post infection. Magnification 40×; scale bar, 500 μm. (B) Quantification of the fluorescence area, 72 h post infection (platelets of n = 3 independent mice, mean ± SD, three images per well). One-way ANOVA; multiple comparisons between A or NA platelets RSD.IFNα with RSD.eGFP within each platelet dilution ∗∗p > 0.01, ∗∗∗∗p > 0.0001. (C) Time course of virus replication measured by the fluorescence area 48, 72, and 144 h post infection (platelets of n = 3–5 independent mice, mean ± SD, three images per well). Two-way ANOVA; multiple comparisons of RSD.IFNα with MeVVac2(GFP) control. ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001.