Figure 3. Preparation and quantification of [U-13C4]AcAc stable isotope internal standard by its synthesis and reduction to [3-D1, U-13C4]βOHB.
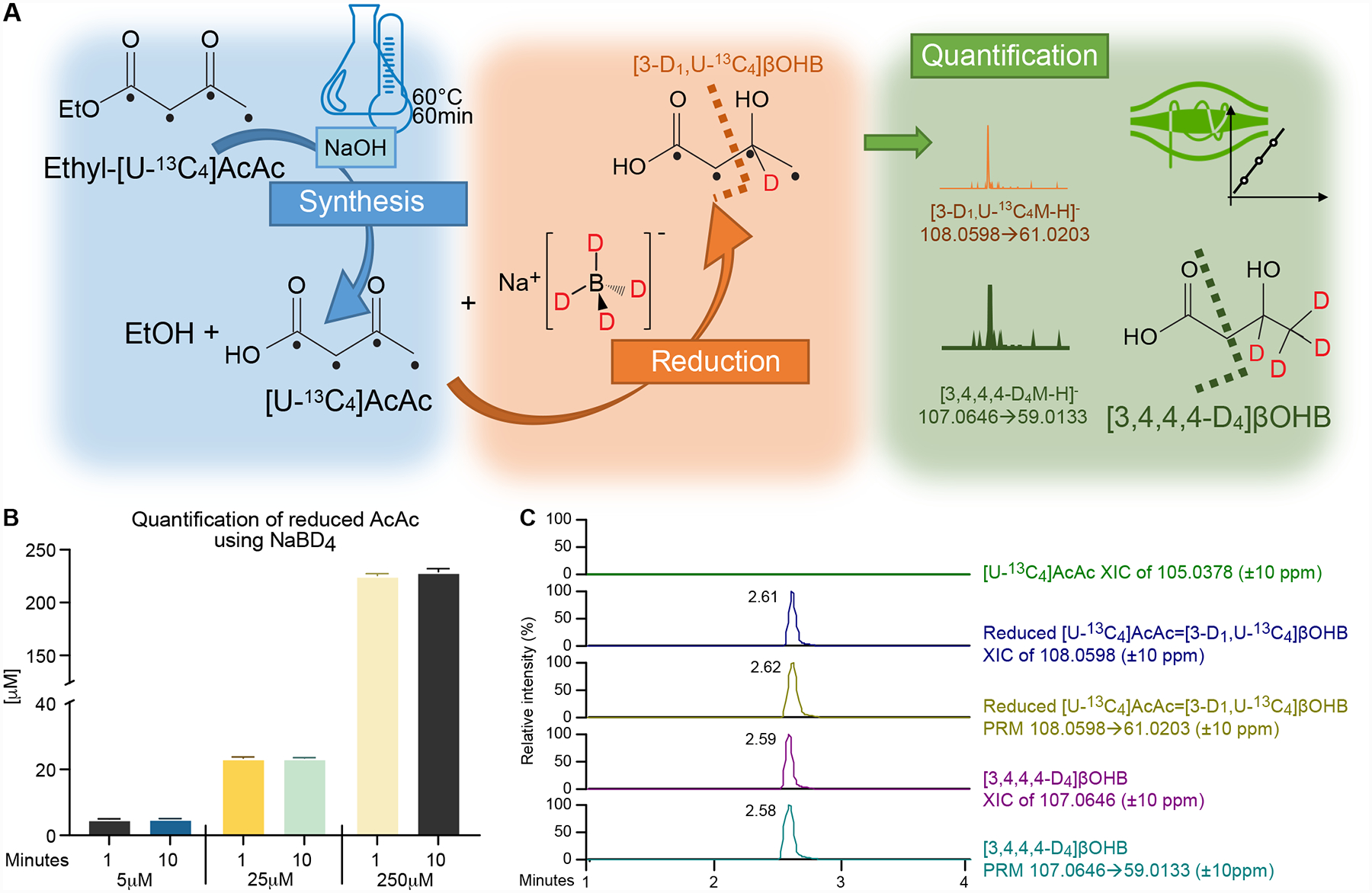
(A) [U-13C4]AcAc is synthetized from ethyl-[U-13C4]AcAc using base-catalyzed hydrolysis. To formally quantify the [U-13C4]AcAc internal standard, synthetized [U-13C4]AcAc is reduced by the reducing agent NaBD4 to [3-D1, U-13C4]βOHB, and quantified using commercially available deuterated [3,4,4,4-D4]βOHB (I.S.) by UPLC-MS/MS method using indicated PRM transitions. Black dots indicate 13C atomic positions. Dashed lines indicate where the molecules are fragmented in HCD chamber. (B) Quantification of [3-D1, U-13C4]βOHB formed from NaBD4-reduction of [U-13C4]AcAc indicates the reaction is rapid and complete across [U-13C4]AcAc starting concentrations (5–250 μM) (n=3/group). (C) NaBD4-reduced extract lacks any residual signal from [U-13C4]AcAc substrate (green XIC of 105.0378, ±10 ppm), while signal attributable to reduced [3-D1, U-13C4]βOHB was observed in Full MS scan (blue XIC of 108.0598, ±10 ppm) and PRM (yellow XIC of 108.0598→61.0203, ±10 ppm) modes. Data was compared to Full MS scan (purple XIC of 107.0646, 10 ppm) and PRM (light blue XIC of 107.0646 → 69.0133, 10 ppm) corresponding to commercially available deuterated [3,4,4,4-D4]βOHB (I.S.). Data are expressed as the mean standard error of the mean (SEM).
