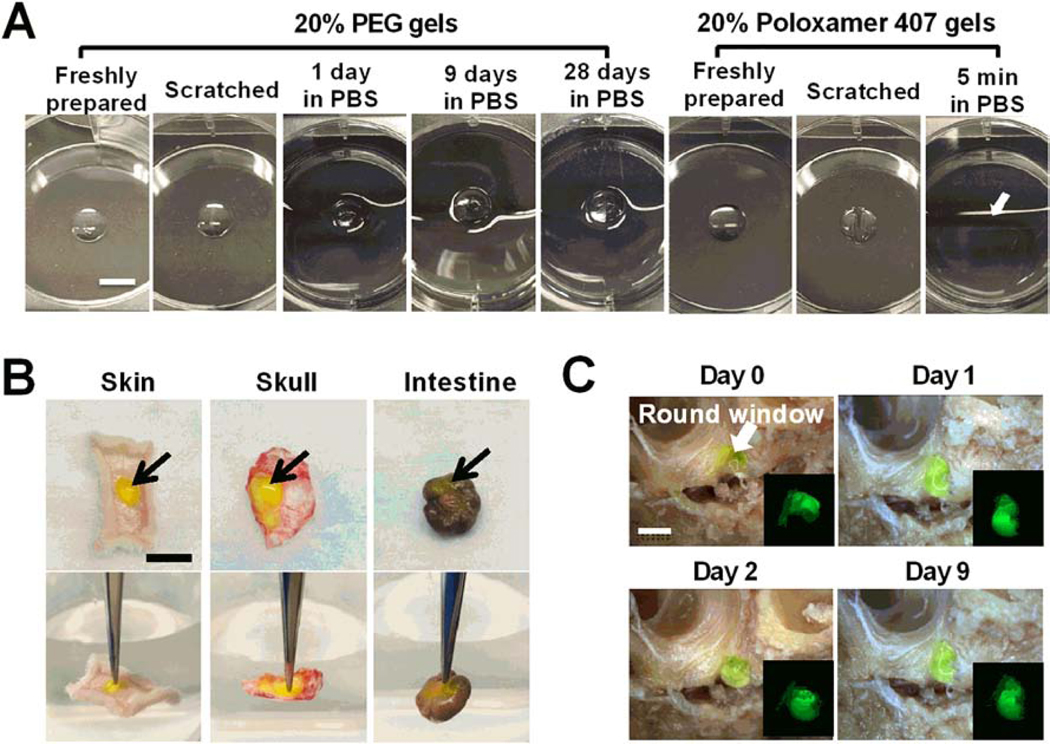
Figure 2. Bioadhesion and in vitro residence time analysis of PEG hydrogels.
(A) Images of freshly prepared PEG and Poloxamer 407 hydrogels and those scratched by a tip or incubated in PBS solutions at 37 °C for the desired times. In situ formed PEG hydrogels bind tightly to tissue culture treated surface and continue to have consistent size in aqueous solutions for over 28 days. Poloxamer 407 hydrogels dissolved in pre-warmed PBS solution within 5 min (The arrow indicates the original location of the hydrogel). Scale bar = 5 mm. (B) Adhesion of in situ formed AF488-labeled 20% PEG hydrogels (green, indicated by arrows) to different fresh tissues, including hypodermis, skull and large intestine. Gels did not detach from the tissue surface when they are lifted with a forceps (the background water level in lower panels indicates the horizontal level). Scale bar = 1 cm. (C) Residence of AF488-labeled 20% PEG hydrogels (green) in the tympanic cavity for over 9 days in PBS solutions. The arrow indicates the round window membrane in the tympanic cavity of middle ear. Scale bar = 5 mm.