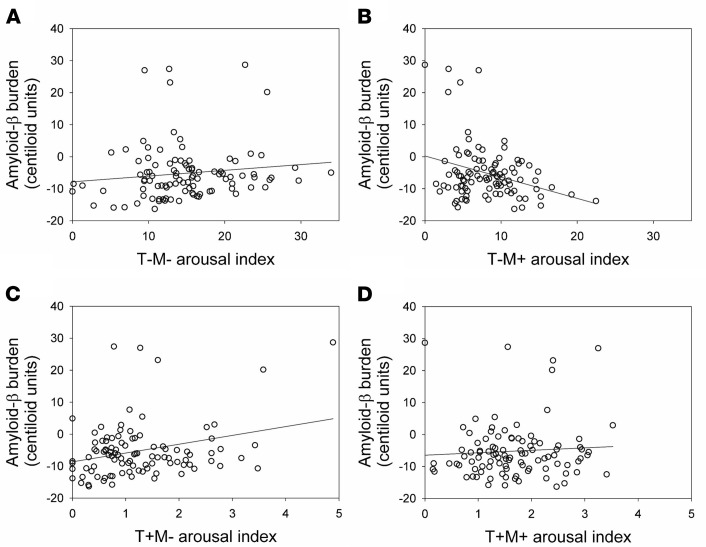
Figure 3. Associations between prevalence of different types of arousals and early cortical Aβ burden.
(A) No correlation between T–M– arousals and Aβ burden (Spearman’s r = 0.16; P = 0.11); (B) significant negative correlation between T–M+ arousals and Aβ burden (Spearman’s r = –0.16, P = 0.11); (C) significant positive correlation between T+M– arousals and Aβ burden (Spearman’s r = 0.17, P = 0.08); and (D) no correlation between T+M+ arousals (Spearman’s r = 0.07, P = 0.46). See main text for full GLMM output controlling for several covariates. T, arousal associated (T+) or not (T–) with sleep stage transition; M, arousal associated (M+) or not (M–) with an increase in EMG tone. Indexes correspond to hourly prevalence.